Difference between revisions of "Drawings"
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
==Permeable Pavements== | ==Permeable Pavements== | ||
| + | |||
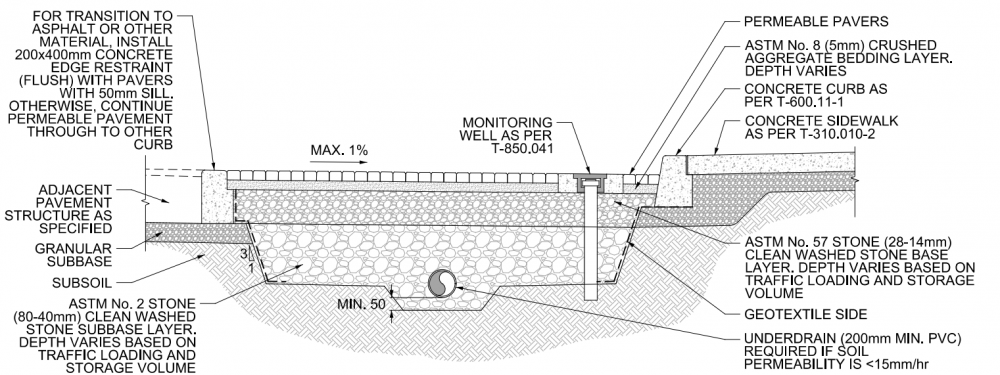
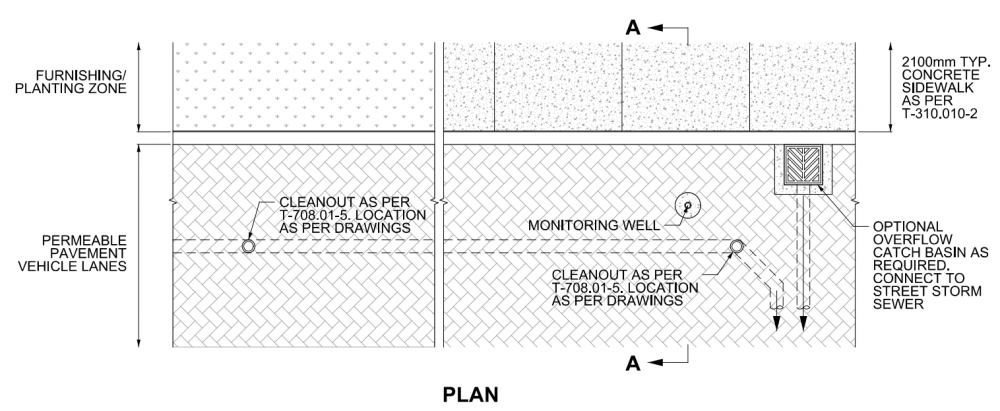
| + | Please see below a profile and plan view of a drawing of a standard permeable pavement composed of interlocking pavers located in a parking lot/laneway, location independent upon estimated traffic and vehicular loading. The installation is designed with an underdrain in this drawing as the site has low permeability (< 15mm/hr), allowing for partial infiltration in the system. The permeable paver installation also includes a cleanout for said underdrain in case of clogging, and is comprised of a crushed aggregate bedding layer, clean washed stone base, and subbase (more about these layers can be found under here [[OPSS aggregates]] & [[Choker layer]]). The entire facility and these layers are surrounded by a geotextile to retain these layers and separate them from the underlying soil subgrade, allowing the system to infiltrate water into the surrounding soil and prevent migration amongst layers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Drawings are from the City of Toronto's, [https://www.toronto.ca/services-payments/building-construction/infrastructure-city-construction/construction-standards-permits/standards-for-designing-and-constructing-city-infrastructure/construction-specifications-drawings-for-green-infrastructure/?accordion=green-infrastructure-drawings Design Criteria for Green Infrastructure in the Right-of-Way] <ref>https://www.toronto.ca/services-payments/building-construction/infrastructure-city-construction/construction-standards-permits/standards-for-designing-and-constructing-city-infrastructure/construction-specifications-drawings-for-green-infrastructure/?accordion=green-infrastructure-drawings Design Criteria for Green Infrastructure in the Right-of-Way </ref> document. For further details about these cross section drawings please visit the link. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Permeable paver profile.PNG|1000px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Permeabel paver plan.PNG|1000px]] | ||
==Rainwater Harvesting== | ==Rainwater Harvesting== | ||
Revision as of 19:19, 1 February 2022
Overview[edit]
Whilst we consider preparing our own set of STEP LID drawings, we are providing a quick reference list to drawing files from other Ontario and/or Canada-based sources.
If you want help in finding example details for an LID design, please email the Wiki Guide email account or use the comment box below.
You know that typical drawings are no substitute for properly configured design!
Ontario Municipal References[edit]
- The City of Toronto Green Streets program included production of many drawn 'typicals'. See example of curb extensions to the right.[1]
- The City of Kitchener has standard details for pervious concrete pavement, precast permeable interlocking pavement and permeable pipe exfiltration systems, a note - you will have to send them an email requesting access to their development manual[2].
- The City of Barrie has a draft standard detail for an exfiltration trench and soakaway pit in Appendix A - Figures of the linked website. Note that the 'within-WHPA' detail is not supported by STEP. [3]
Exfiltration Systems[edit]
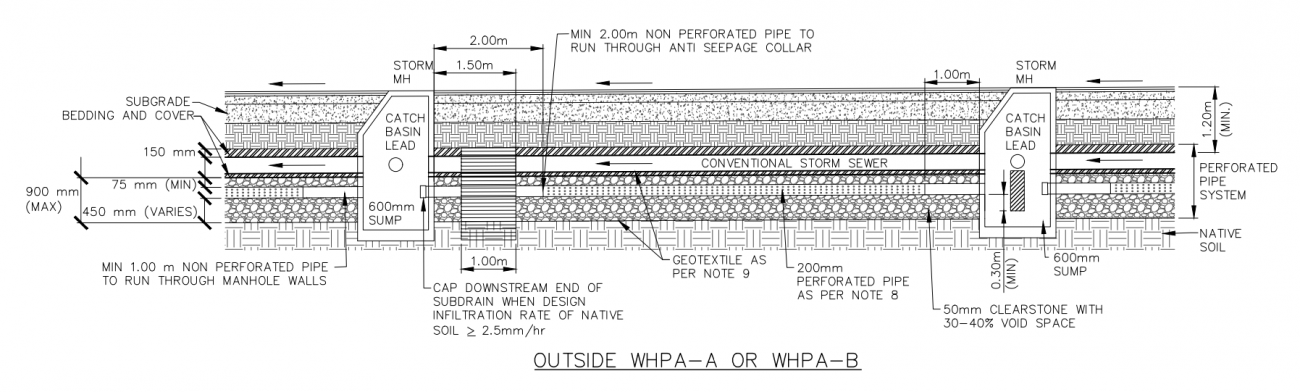
Please see below a Profile view of an exfiltration system (or perforated pipe system) designed for use in the city of Barrie and used in conjunction with a typical storm sewer system. Note: This cross section installment is 'not located within a WHPA', although the source document for this drawing showcases a similar design configuration, that is 'located within a WHPA', which is not supported by STEP.
Drawings are from the City of Barrie's, Drainage Master Plan [4] document. For further details about these cross section drawings please visit the link.
Infiltration Trenches/Chambers & Soakaways[edit]
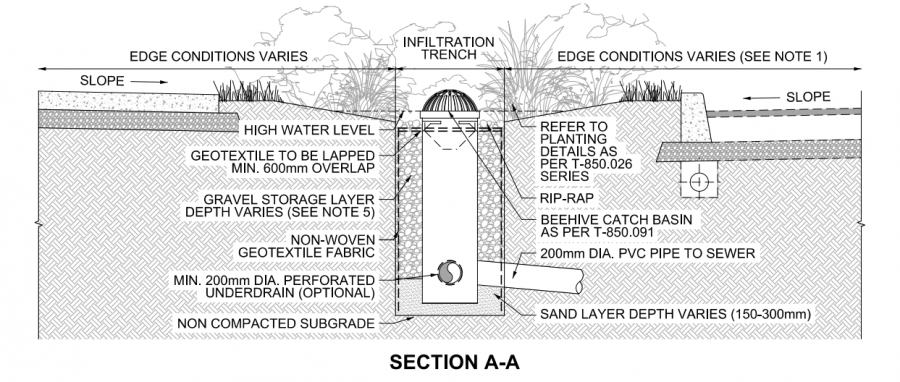
Please see below a profile and plan view of an infiltration trench designed to treat and temporarily store stormwater for use in the City of Toronto located within the laneway between the road and sidewalk in a heavily urbanized location. This drawing depicts partial exfiltration where remaining stormwater runoff is directed to the nearby storm sewer system.
Drawings are from the City of Toronto's, Design Criteria for Green Infrastructure in the Right-of-Way [5] document. For further details about these cross section drawings please visit the link.
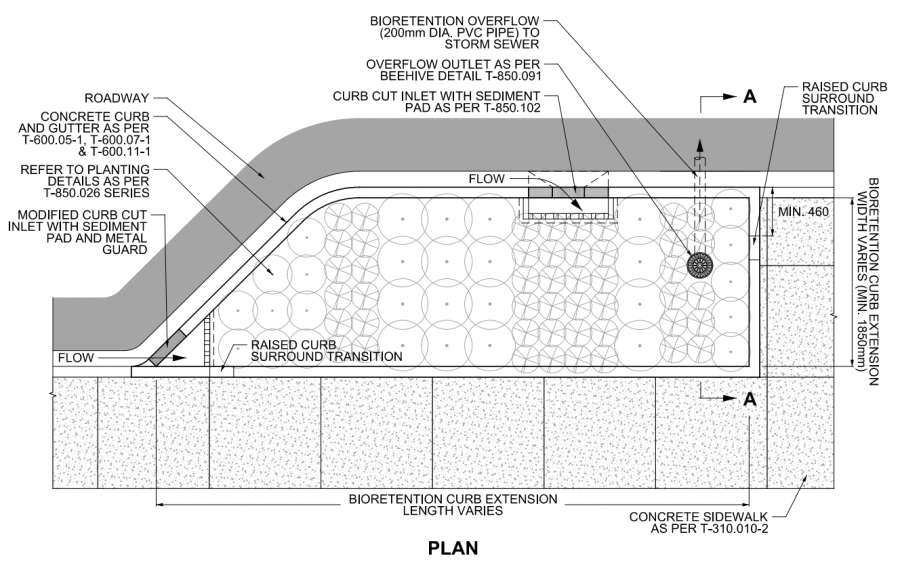
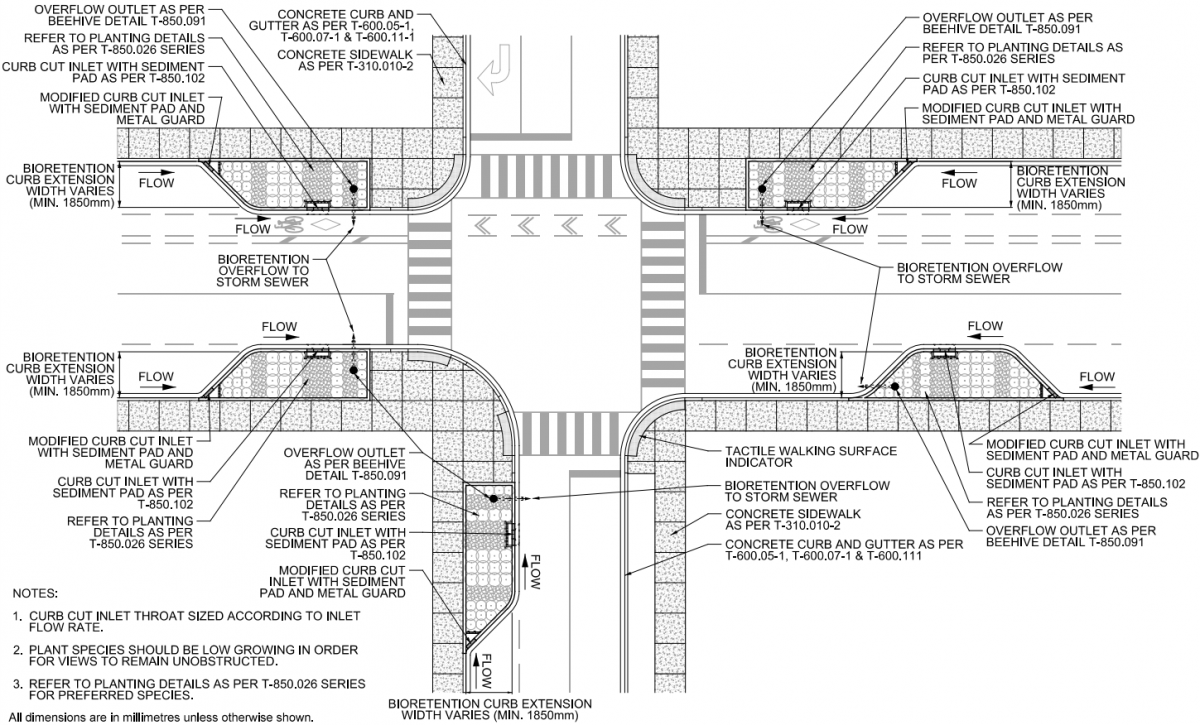
Bioretention[edit]
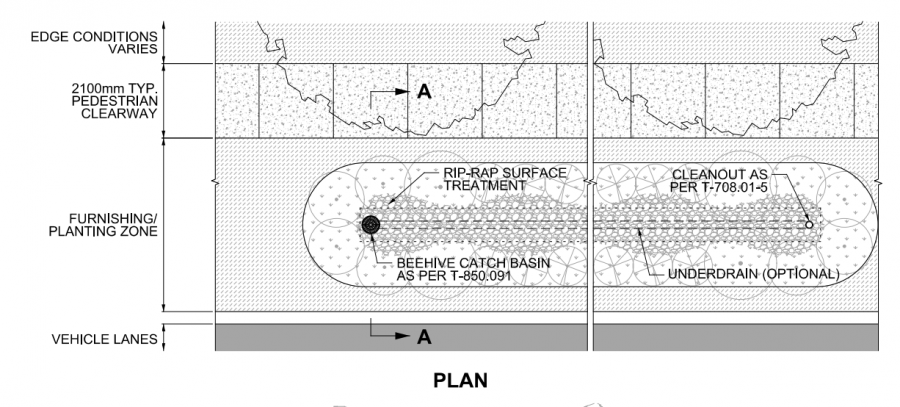
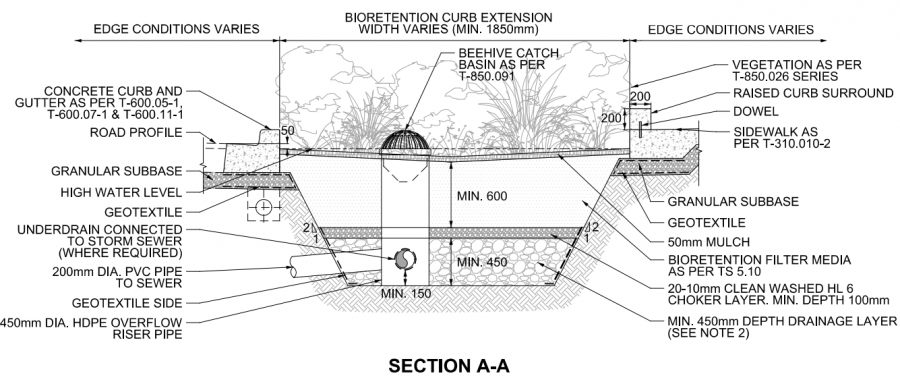
Please see below a profile and plan view (along with a larger scale intersection plan view) of a bioretention facility designed in an urban curb extension/"bump-out" designed to both calm traffic, enhance green space in an urban setting and treat overflow/runoff from the nearby street. Given that the bioretention is bound entirely with impermeable hardscape there is limited options for pretreatment. In the cross-sections shown below the pretreatments included in the installation are the inclusion of sediment traps sediment traps - a type of forebay, which dissipates incoming flow into the feature and causes suspended sediment to settle out of the water. This allows for accumulated sediment to be cleaned out during general maintenance of the bioretention feature.
An excellent opportunity for integrating more bioretention into the street is through careful design of curb extensions for traffic control [6]. See Roadside safety for design advice specific to this application. This drawing also depicts partial exfiltration with an installed underdrain as soils in this feature possess infiltration rates lower than 15mm/hr, and possesses several plantings. Remaining stormwater runoff is directed to the nearby storm sewer system.
Drawings are from the City of Toronto's, Design Criteria for Green Infrastructure in the Right-of-Way [7] document. For further details about these cross section drawings please visit the link.
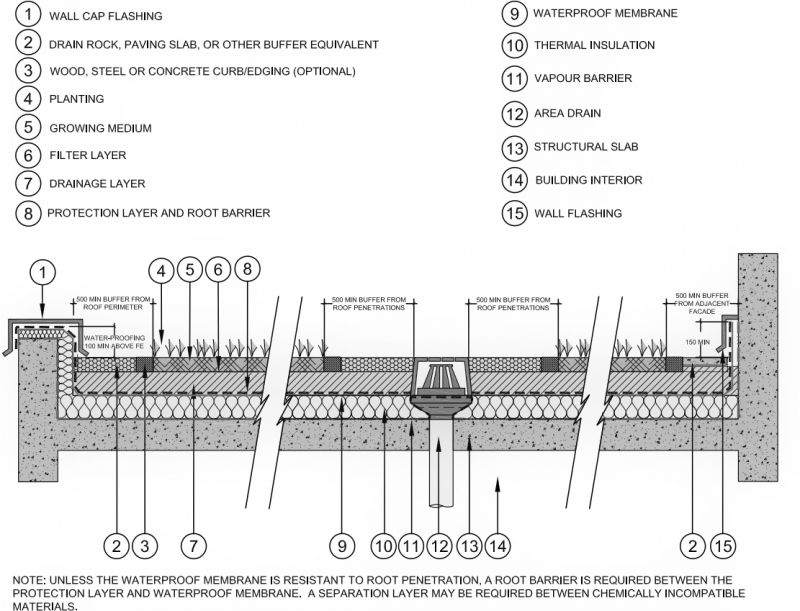
Green Roof[edit]
Please see below a profile view of a standard extensive green roof with a stone buffer layer, growing medium, filter layer, drainage layer, root barrier/protection layer, waterproof membrane and vapour barrier. What makes the following drawing an extensive green roof is that it consists of a thinner planting medium layer ( ≤15 cm deep) with herbaceous vegetative cover that possess shallower root systems and is designed for SWM purposes, and generally don't provide public access.
Drawing is from Metro Vancouver's, Stormwater Source Control Design Guidelines document [8] document. For further details about these cross section drawings please visit the link.
Permeable Pavements[edit]
Please see below a profile and plan view of a drawing of a standard permeable pavement composed of interlocking pavers located in a parking lot/laneway, location independent upon estimated traffic and vehicular loading. The installation is designed with an underdrain in this drawing as the site has low permeability (< 15mm/hr), allowing for partial infiltration in the system. The permeable paver installation also includes a cleanout for said underdrain in case of clogging, and is comprised of a crushed aggregate bedding layer, clean washed stone base, and subbase (more about these layers can be found under here OPSS aggregates & Choker layer). The entire facility and these layers are surrounded by a geotextile to retain these layers and separate them from the underlying soil subgrade, allowing the system to infiltrate water into the surrounding soil and prevent migration amongst layers.
Drawings are from the City of Toronto's, Design Criteria for Green Infrastructure in the Right-of-Way [9] document. For further details about these cross section drawings please visit the link.
Rainwater Harvesting[edit]
Enhanced Swales / Bioswales[edit]
Stormwater Tree Trenches[edit]
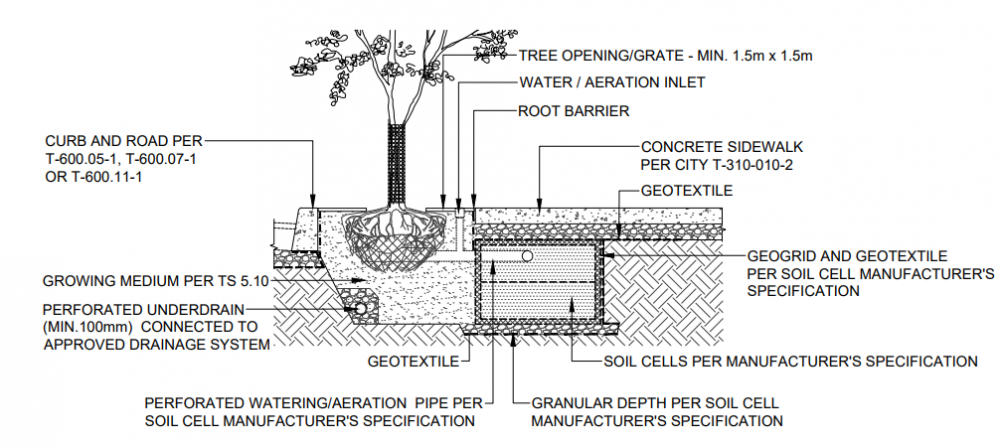
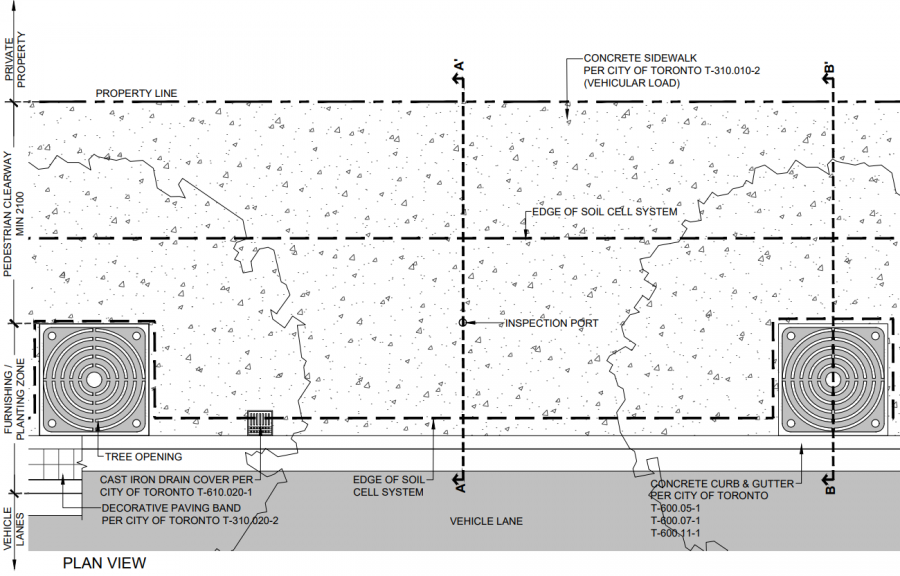
Please see below a Plan and Profile view of one of several variations of a stormwater planter (soil cell) along a roadway. This type of cross section installment showcases a tree trench in a continuous growing medium located under a hard boulevard/concrete surface that can withstand constant and heavy vehicular loads. Drawings are from the City of Toronto's Green Streets Technical Guidelines Appendices document. For further details about these cross section drawings please visit the link.
External Drawing Cross Sections[edit]
- Oregon State University LID typicals by GreenGirl
- Plan drawings by Low Impact Development Center, Inc.
- Bioretention detail by Philly Water
- Permeable paving by Philly Water
- Pipe-in-stone infiltration by Philly Water
Proprietary[edit]
In our effort to make this guide as functional as possible, we have decided to include proprietary systems and links to manufacturers websites.
Inclusion of such links does not constitute endorsement by the Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program.
Lists are ordered alphabetically; link updates are welcomed using the form below.
- ADS pipe
- Soil cells by Silvacell
- pretreatment by Hydro International
- ↑ https://www.toronto.ca/services-payments/streets-parking-transportation/enhancing-our-streets-and-public-realm/green-streets/
- ↑ https://www.kitchener.ca/en/development-and-construction/development-manual.aspx
- ↑ https://www.barrie.ca/City%20Hall/Planning-and-Development/Engineering-Resources/Pages/Infrastructure-Master-Plans.aspx
- ↑ https://www.barrie.ca/City%20Hall/Planning-and-Development/Engineering-Resources/Documents/Drainage-Master-Plan/Appendices/Appendix%20A%20-%20Figures.pdf
- ↑ https://www.toronto.ca/services-payments/building-construction/infrastructure-city-construction/construction-standards-permits/standards-for-designing-and-constructing-city-infrastructure/construction-specifications-drawings-for-green-infrastructure/?accordion=green-infrastructure-drawings Design Criteria for Green Infrastructure in the Right-of-Way
- ↑ https://greenactioncentre.ca/healthy-travel/traffic-calming-101/#:~:text=A%20curb%20extension%2C%20or%20curb,to%20reduce%20speed%20(above)
- ↑ https://www.toronto.ca/services-payments/building-construction/infrastructure-city-construction/construction-standards-permits/standards-for-designing-and-constructing-city-infrastructure/construction-specifications-drawings-for-green-infrastructure/?accordion=green-infrastructure-drawings Design Criteria for Green Infrastructure in the Right-of-Way
- ↑ http://www.metrovancouver.org/services/liquid-waste/LiquidWastePublications/StormwaterSourceControlDesignGuidelines2012StormwaterSourceControlDesignGuidelines2012.pdf Stormwater Source Control Design Guidelines
- ↑ https://www.toronto.ca/services-payments/building-construction/infrastructure-city-construction/construction-standards-permits/standards-for-designing-and-constructing-city-infrastructure/construction-specifications-drawings-for-green-infrastructure/?accordion=green-infrastructure-drawings Design Criteria for Green Infrastructure in the Right-of-Way