Difference between revisions of "Bioretention: Partial infiltration"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
rect 1296 1423 1348 1478 [[Underdrains|Underdrain Access Structure]] | rect 1296 1423 1348 1478 [[Underdrains|Underdrain Access Structure]] | ||
rect 1293 3128 1346 3178 [[Underdrains|Underdrain]] | rect 1293 3128 1346 3178 [[Underdrains|Underdrain]] | ||
| + | rect 1134 3187 1159 3246 [[Digital technologies|Water Level Sensor]] | ||
rect 1112 3181 1169 3250 [[Bioretention: Internal water storage|Internal Water Storage]] | rect 1112 3181 1169 3250 [[Bioretention: Internal water storage|Internal Water Storage]] | ||
| − | |||
rect 1126 2838 1163 3187 [[Wells|Monitoring Well]] | rect 1126 2838 1163 3187 [[Wells|Monitoring Well]] | ||
rect 1116 1437 1163 1480 [[Wells|Monitoring Well]] | rect 1116 1437 1163 1480 [[Wells|Monitoring Well]] | ||
| − | rect 1295 3183 1348 3254 [[Bioretention|Water Storage | + | rect 1295 3183 1348 3254 [[Bioretention: Internal water storage|Internal Water Storage]] |
rect 939 1415 1011 1482 [[Overflow|Overflow Outlet]] | rect 939 1415 1011 1482 [[Overflow|Overflow Outlet]] | ||
rect 956 2845 1017 3177 [[Overflow|Overflow Outlet]] | rect 956 2845 1017 3177 [[Overflow|Overflow Outlet]] | ||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
*[[Erosion control blankets|Erosion control]] | *[[Erosion control blankets|Erosion control]] | ||
*[[Mulch]] | *[[Mulch]] | ||
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Planting design|Planting considerations]] and [[Plant lists| Recommended species]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Clickable button|[[Bioretention cells|Back to Bioretention]]}} | {{Clickable button|[[Bioretention cells|Back to Bioretention]]}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
[[category: Infiltration]] | [[category: Infiltration]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:25, 27 September 2022

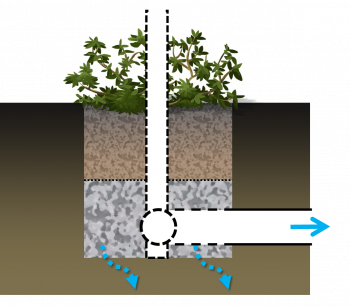
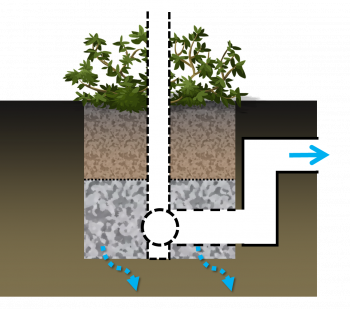
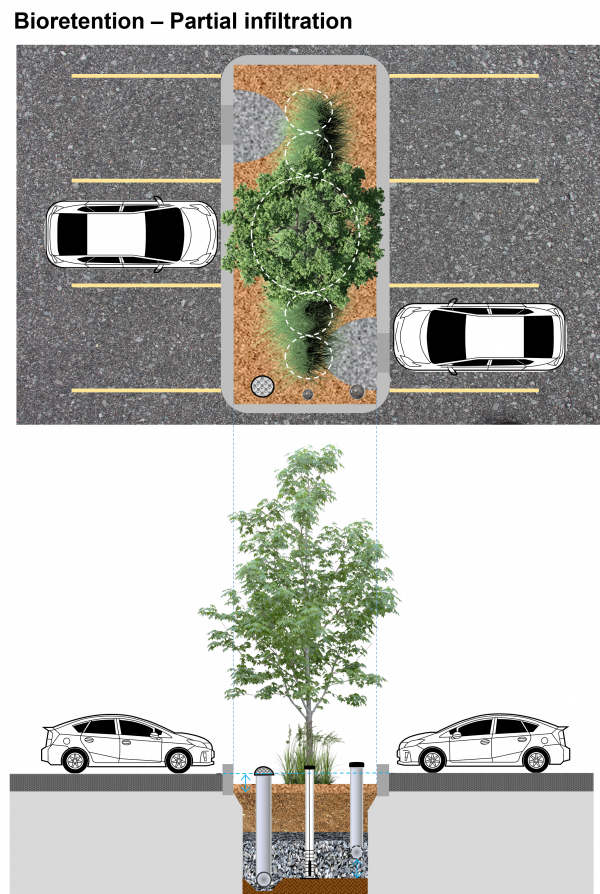
Partial infiltration bioretention cell draining a parking lot. This design variation includes an underdrain and surface overflow pipes that allow excess water to leave the practice. A monitoring well is included so drainage performance can be evaluated over its operating lifespan. For more details on this variation of a bioretention feature and others, click here for the City of Toronto's Green Streets Technical Guidelines (GSTG).,[1] Note: The following is an "image map", feel free to explore the image with your cursor and click on highlighted labels that appear to take you to corresponding pages on the Wiki.
Overview[edit]
Over soils with slow infiltration rates, it is advantageous to drain a portion of the stored water prior to any upcoming storm. This popular design choice can optimize annual water balance, mitigate peak flow rates and by ensuring water flow through, can reduce the accumulation of sodium and chlorine ions from winter salting.
Partially infiltrating bioretention with underdrain.
Partially infiltrating bioretention with anaerobic/aerobic storage zone.
Materials[edit]
References[edit]
- ↑ City of Toronto. 2017. City of Toronto's Green Streets Technical Guidelines - Version 1.0. Schollen & Company Inc., Urban Forest Innovators, TMIG, DMG. August, 2017. https://www.toronto.ca/legdocs/mmis/2017/pw/bgrd/backgroundfile-107514.pdf