Difference between revisions of "Monitoring"
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
| − | Stormwater practices suitable for functional monitoring may include ones that: | + | Stormwater practices suitable for ''''functional monitoring'''' may include ones that: |
| − | # | + | # Have [[Inspection and Maintenance: Underground Infiltration Systems|underground drainage pathways]] that may not be captured through visual inspections; |
| − | # | + | # Have undergone design modifications during construction that may have influenced system function; |
| − | # | + | # Were identified during visual inspections as having potential deficiencies; |
| − | # | + | # Could benefit from additional monitoring to refine planned maintenance programs or elucidate system response and function during [[Understanding rainfall statistics|rain events]] of varying size. |
| + | |||
| + | Stormwater practices that may be suitable for ''''performance monitoring'''' may include: | ||
| + | # New technologies for which detailed monitoring data are needed to verify performance against design criteria and/or provide information on potential design improvements for future site applications; | ||
| + | # Technologies or series of technologies configured or installed in a unique way for which detailed monitoring data are needed to understand performance; | ||
| + | # Projects designed as a pilot demonstration with specific learning outcomes that could be transferred to future sites with similar technologies or management measures. | ||
Revision as of 15:56, 11 March 2024
Overview[edit]
An inspection and monitoring program is a fundamental part of implementing stormwater management plans and operating facilities. The program evaluates whether a stormwater management practice or system is constructed and functioning according to design and meets the environmental and public health and safety objectives it was designed to meet.
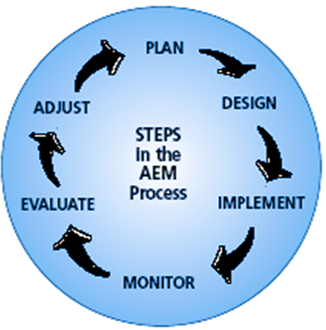
Detailed inspections and monitoring during and after project implementation also help identify potential problems before they grow into larger issues and provide project management staff with opportunities to learn from mistakes and improve processes and designs in future projects. This process of continuous learning and improvement is often referred to as ‘adaptive management’ which ‘promotes flexible decision making that can be adjusted in the face of uncertainties as outcomes from management actions and other events become better understood’ (this can be seen in the image above).
It is important to view inspections and monitoring as part of a single program that strives to meet overlapping goals and shares the same overarching objective of continuous learning and improvement. Key types of inspections and monitoring initiatives include:
- Construction inspections: These inspections are conducted by qualified staff just prior to construction of stormwater feature and at intervals throughout construction corresponding to major milestones such as the completion of excavation, connection of drainage pipes, media placement, etc. Approved erosion and sediment control plans and site/feature design drawings provide the benchmark against which construction outcomes are evaluated.
- Assumption inspections: These inspections assess whether the stormwater management practice has been constructed in accordance with the design drawings and that approved design modifications (if any) meet expectations. These inspections are conducted after substantial completion of construction prior to the beginning of the ‘warranty period’ (typically 2 years), and again at the end of the ‘warranty period’ and prior to final assumption of ownership by the municipality or owner.
- Routine operation and verification inspections: These inspections are conducted by maintenance crews after assumption of the facility and are typically followed by various maintenance tasks identified as necessary to restore the visual appeal of the practice and ensure any functional issues are addressed. Routine Inspections occur at regular intervals throughout the year, while verification inspections entail more detailed assessments conducted periodically (e.g. every 5 years) to evaluate whether minor or major repairs are needed to rehabilitate overall system function.
- Functional monitoring: This type of monitoring is often conducted with continuous measurement devices (e.g. water level sensors, water temperature sensors) over a period of time to evaluate the function of the system during and after rain events. Typical functional monitoring parameters may include inlet and outlet function, surface and subsurface water level changes, overflow frequency and soil moisture/salinity conditions (see below for more details). Functional monitoring may occur any time after substantial completion of construction. Conducting functional monitoring during the warranty period can simplify and/or replace the tasks needed for assumption inspections, since the former can be regarded as a more detailed form of an assumption inspection.
- Performance monitoring: This monitoring evaluates how well a stormwater management feature or management measure performs in comparison with a range of performance indicators or design targets (e.g. peak flow attenuation, volume reduction) to determine whether design criteria has been met and to compare how this practice performs relative to other stormwater facilities, technologies and/or development contexts. This more detailed monitoring would typically occur after the development site has been stabilized either before or after site assumption by the municipality or owner. Conducting performance monitoring after substantial completion of construction can replace and/or simplify the tasks typically undertaken through both functional monitoring and assumption inspections because performance monitoring involves a wide range of detailed measurements, including many of the same measurements undertaken through simpler inspection and monitoring programs.
- Environmental effects monitoring: This monitoring is designed to assess the cumulative impact of land use changes and stormwater management measures on groundwater, terrestrial system and/or the environmental health of a stream reach, subwatershed, watershed, or individual community. Understanding environmental effects requires quantifying key sources of hydrologic and chemical changes within the contributing drainage area, monitoring the major management measures put in place to mitigate land use changes, and evaluating changes in physical, chemical and biological indicators of the environmental systems of interest (e.g. groundwater, receiving waters, terrestrial systems). Where budget is limited, an environmental effects monitoring program may be scoped to evaluate impacts on a limited range of environmental variables (e.g. stream health, groundwater contamination).
Inspections[edit]
Detailed guidance on the various types of inspections required as part of a comprehensive inspection and maintenance plan is provided on the wiki inspection and maintenance page here:
Monitoring[edit]
Unlike centralized stormwater management facilities, the LID approach involves the installation of many smaller stormwater management practices distributed across the landscape. Therefore, it is often not cost effective to conduct functional and/or performance monitoring of every practice.
For this reason, an effective monitoring program will ensure that all practices undergo the inspections detailed above, but only representative practices are selected for continuous functional and/or performance monitoring. Since functional monitoring is relatively simple and cost effective to undertake, it may be applied to a larger number of features than would be possible if more quantitative data on performance was required. Detailed performance monitoring should be reserved only for new technologies or new configurations of practices for which local data on performance is lacking.
Stormwater practices suitable for 'functional monitoring' may include ones that:
- Have underground drainage pathways that may not be captured through visual inspections;
- Have undergone design modifications during construction that may have influenced system function;
- Were identified during visual inspections as having potential deficiencies;
- Could benefit from additional monitoring to refine planned maintenance programs or elucidate system response and function during rain events of varying size.
Stormwater practices that may be suitable for 'performance monitoring' may include:
- New technologies for which detailed monitoring data are needed to verify performance against design criteria and/or provide information on potential design improvements for future site applications;
- Technologies or series of technologies configured or installed in a unique way for which detailed monitoring data are needed to understand performance;
- Projects designed as a pilot demonstration with specific learning outcomes that could be transferred to future sites with similar technologies or management measures.