Difference between revisions of "Filtration Manufactured Treatment Devices"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
Further guidance on how the data and information generated from verified field testing of Filtration MTDs should be interpreted and factored into regulatory agency approvals and procurement decisions for stormwater management is provided in this [https://sustainabletechnologies.ca/app/uploads/2023/06/SETV-Guidance-PAS-2023-06-01-French-1.pdf Publicly Available Specification] that addresses both OGS and Filtration MTDs. | Further guidance on how the data and information generated from verified field testing of Filtration MTDs should be interpreted and factored into regulatory agency approvals and procurement decisions for stormwater management is provided in this [https://sustainabletechnologies.ca/app/uploads/2023/06/SETV-Guidance-PAS-2023-06-01-French-1.pdf Publicly Available Specification] that addresses both OGS and Filtration MTDs. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 22:23, 6 February 2024
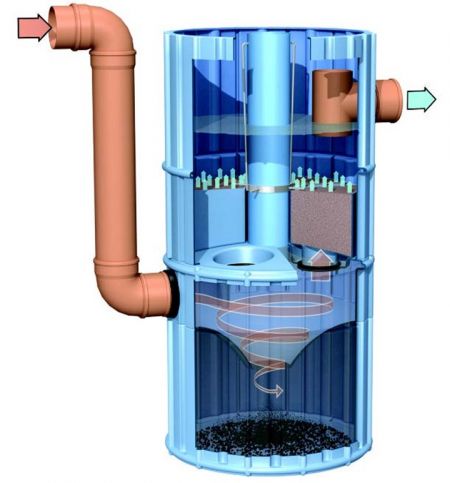
Overview[edit]
Filtration Manufactured Treatment Devices (MTDs) are structures with one or more chambers containing filtration media, membranes and/or filtration cartridges that remove solids and debris/trash from runoff. Some units may have oil separation functions and pretreatment chambers for coarse sediment and debris. The filter components are designed to remove the coarse and fine sediment fraction of suspended solids and associated pollutants in stormwater runoff and may also target removal of dissolved pollutants such as phosphorus or metals through biological and/or chemical processes.

Application[edit]
Filtration MTDs are suitable for pre-treatment or may be installed as stand alone if third party performance testing shows that they achieve enhanced level water quality protection (i.e. lower 95th percentile removal efficiencies of 80% or greater).
Since Filtration MTDs contain filters that restrict flow rates, they are normally designed for much lower hydraulic loading rates than Oil-Grit Separator MTDs and have longer detention times. Flow restriction occurs due to the small pore size openings of filters and the clogging of pores and/or the formation of films either on the surface of the filter or within the filter matrix filter. For this reason, inspection and maintenance intervals for Filtration MTDs are normally shorter than for OGS MTDs. The method of maintenance typically involves sediment removal with a hydro vacuum truck as well as filter cleaning or replacement.
Further guidance on how the data and information generated from verified laboratory testing of OGS technologies should be interpreted and factored into regulatory agency approvals and procurement decisions for stormwater management is provided in this publicly available specification The Canadian Procedure for Field Testing of Stormwater Filtration Manufactured Treatment Devices, developed by TRCA and the Standards Council of Canada that addresses both OGS and Filtration MTDs.
Further guidance on how the data and information generated from verified field testing of Filtration MTDs should be interpreted and factored into regulatory agency approvals and procurement decisions for stormwater management is provided in this Publicly Available Specification that addresses both OGS and Filtration MTDs.
- ↑ 3P Technik UK Ltd. 2023. HYDROSYSTEM1000 SUDS MULTI-PROCESS TREATMENT DEVICE. Multi-process SUDS Treatment Device Stages. Accessed: https://www.3ptechnik.co.uk/stormwater-treatment/hydrosystem_1000/
- ↑ STEP. 2020. Performance Evaluation of a High Rate Treatment Bioretention Filter Multi-process SUDS Treatment Device Stages. Technical Brief. Accessed: https://sustainabletechnologies.ca/app/uploads/2020/06/High-rate-treatment-bioretention-filter-tech-brief.pdf