Overview[edit]
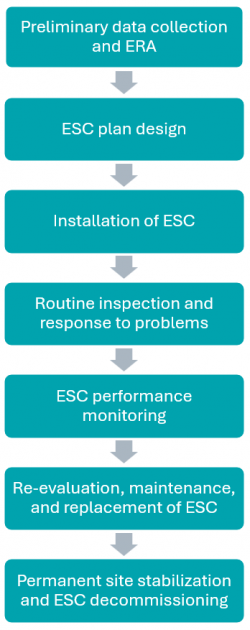
Effective ESC starts before
topsoil stripping begins. This flow chart shows the ESC process from construction project start to finish. Scroll through the wiki to read about each step of the process.
Erosion and sediment controls (ESC) are technologies, practices and procedures that are applied to prevent the release of sediment from construction sites. Rapid urban expansion and associated construction activities are a significant source of stress to the natural environment. As construction processes involve the removal of vegetation and de-stabilization of soils, they can accelerate natural processes of erosion and sedimentation, mobilizing more sediment and associated contaminants that can ultimately end up in downstream receiving water systems. ESC measures are essential to help reduce these sediment loads from active construction sites and protect downstream aquatic habitats from becoming impaired.
Inadequate ESC during construction can cause:
- sediment-laden runoff to enter downstream and adjacent natural features, including streams, lakes, wetlands and woodlots;
- deposition of sediment on adjacent private property and roadways;
- clogging of onsite stormwater management systems and LIDs;
- expensive cleanup and restoration costs;
- delays or stop-work orders; and
- fines from regulatory agencies.
Implementing effective ESC practices throughout all stages of construction is essential to sustainable urban growth and ensuring regulatory compliance.

The Toronto and Region Conservation Authority, through
STEP, published the
Erosion and Sediment Control Guide for Urban Construction in 2019. This wiki page summarizes key content from the guide and provides additional resources; however, readers should consult the full guide for comprehensive information. Click on the image to access the guide (
STEP, 2019)
[1].
Erosion risk assessments (ERA)[edit]
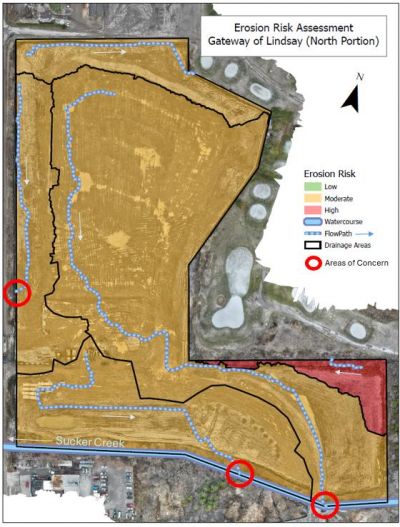
ERAs divide a project site into areas of low, medium, and high erosion risk to optimize ESC placement. Kawartha Conservation used drones to map erosion risk on this site, helping to protect Sucker Creek other local water bodies from construction-related
sediment runoff. Click the image to learn more (Kawartha Conservation, 2025)
[2].
To manage the potential negative impacts of construction activities in the absence of effective ESC measures, Erosion Risk Assessments (ERAs) are conducted to guide the selection and placement of appropriate ESC practices on site.
ERAs are recommended when:
- the extent of land disturbance is greater than 10 ha and duration is longer than 30 days, or
- construction activities are planned in or near natural water features, or
- the site drains to species at risk habitat
The hybrid qualitative ERA approach is recommended in the above situations, except where local regulatory agencies require a different approach. The hybrid qualitative ERA approach estimates erosion risk by dividing a site into areas based on soil, slope, and ground cover, then rating each area as low, moderate, or high erosion risk to help choose the right erosion control practices for each stage of construction. Completing an ERA demonstrates due diligence, identifies high-risk areas early, informs effective BMP selection and placement, guides the use of enhanced controls, and provides context for decision-making. To learn more about ERAs, read section 6.2 in the Erosion and Sediment Control Guide for Urban Construction (2019).
ESC plan design[edit]
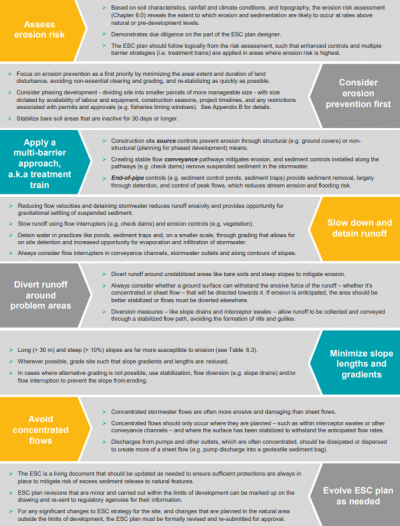
Overview of ESC planning principals.
An ESC plan should be created based on a given site’s ERA, with more controls used in the higher risk areas.
An ESC plan should be designed for each stage of construction:
- Topsoil stripping, grading, and stabilization
- Servicing
- Building construction
- Final stabilization/rehabilitation and ESC decommissioning
An ESC plan should include drawings, standard notes and reports depicting and describing the site conditions (e.g. grades, locations of natural features, soil stockpiles and other key points of interest) during each phase of construction, and the BMPs that will be
applied to mitigate erosion and sediment transport.
Types of ESC[edit]
Erosion controls
• prevent exposed soils from being entrained by water or wind
• address sediment at its source
Sediment controls
• remove sediment suspended in stormwater through settling and filtration
The most effective application of ESC utilizes a multi-barrier approach, in which erosion controls and sediment controls are installed in sequence to form a resilient system that protects the natural environment from sediment-related impacts. A multi-barrier system incorporates built-in redundancy, ensuring that if one control fails, additional measures remain in place to safeguard downstream features. Selecting appropriate BMPs for each project stage requires an understanding of their function, intended use, expected performance, and maintenance needs. Note: Isolation measures are not covered on this page but are detailed in the 2019 Erosion and Sediment Control Guide for Urban Construction.
Table 1 and 2 provide an overview of common erosion and sediment controls. Click on the BMP name in the first column to read the detailed design requirements and installation, inspection, maintenance, and decommissioning guidance from the 2019 Erosion and Sediment Control Guide for Urban Construction. A description and common applications of each practice are listed in the second and third columns, respectively. The fourth column provides additional resources and the fifth column shows an example image of the BMP.
Good and poor examples of ESC installation are shown on the right side. Additional examples can be found on the pre-construction wiki.
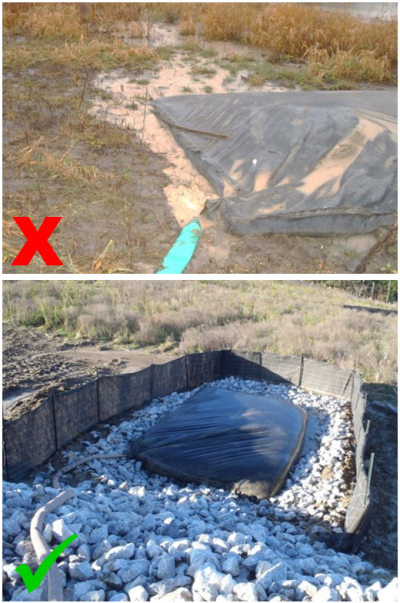
Erosion controls[edit]

An interceptor
swale should be stabilized with a suitable
erosion control BMP (e.g., vegetation or RECP), particularly if it will be in place for more than 30 days. In order to reduce the potential for
swale erosion and provide opportunity for
sediment settling, flow interruption devices (e.g.
check dams, filter socks, coir logs) should be properly installed within the
swales.

Rolled
erosion control products (RECP) should be installed according to manufacturer instructions. In general, RECP on steep slopes should be installed down the slope, extend to the top of the slope, use an anchor trench at top and bottom, be in continuous contact with soil surface and overlap. RECP installed in ditches/channels should be installed parallel to flow direction, be anchored to top of slope on both sides, be in continuous contact with soil surface, and overlap. Air pockets between the RECP and soil will allow stormwater to pass through and erode the soil below.
Table 1. Erosion controls
| BMP (click for more information)
|
Description
|
Applicability
|
Drawings and Additional Resources
|
Example Image
|
| Minimized or Phased Land Clearing
|
Preservation of vegetated areas intercepts and infiltrates rainfall.
|
Areas not being immediately developed on larger sites (>10 ha)
|
Tree Protection Barrier
|
|
| Vegetated Filter Strips
|
Gently sloping, vegetated areas that slow and filter runoff.
|
Areas that may benefit from leaving vegetation in place
|
Vegetated filter strip design Wiki
|
Source: Trinkhaus Engineering
|
| Slope Drains
|
Flexible pipe that conveys water down a disturbed slope to prevent erosion from concentrated runoff.
|
Exposed (and especially long or steep) slopes that convey concentrated flow
|
|
|
| Interceptor Swales
|
Stabilized flow path that conveys runoff away from bare soil to sediment control measures.
|
Any unstabilized areas, but especially where:
- Upslope drainage area is greater than 2 ha
- Slope² × Length ≥ 0.75 m
- In conjunction with slope drains
- Perimeter of site or stabilized/restored areas
- Toe of slopes
- Adjacent to valley/stream corridors
|
Interceptor Swale Diagram
|
|
| Outlet Protection
|
Energy dissipation devices or surface hardening that prevents scour erosion at outlets.
|
Base of any outlet releasing concentrated flow
|
Storm Drain Outfall Protection Diagram
Baffle shapes and size analysis
|
|
| Mulching
|
Layer of organic material (e.g., straw, bark, wood shavings, paper fibre, compost) that absorbs rainfall and acts as a physical barrier to erosion.
|
- Short term on bare soil not subject to concentrated flows
- Dry mulch best where not seeded
- Only apply Hydro-mulch (with tackifier) alone for temporary erosion control
- In conjunction with a tackifier/seeding on slopes steeper than 2H:1V
|
|
|
| Seeding
|
Application of seed to establish vegetation for soil stability.
|
Click to expand.
|
|
|
| Surface Roughening
|
Creates uneven surfaces and depressions to reduce runoff velocity, trap sediment, keep seed in place, and improve vegetation establishment
|
- Inactive (<30 days) disturbed surfaces
- Exposed slopes, especially steeper than 3H:1V and H>1.5 m
- Where vegetation cannot be established
- In conjunction with mulching/seeding
|
Surface roughening diagram for slopes steeper than 3H:1V and H > 1.5 m
Surface roughening for slopes steeper than 2H:1V using bulldozer (Virginia Department of Environmental Quality)[3]
|
|
| Rolled Erosion Control Products
|
Netting, blankets, or turf reinforcement mats act as a physical barrier to erosion. Biodegradable options free of plastic netting prevent wildlife ensnaring.
|
- Bare areas that convey concentrated flows
- Slopes steeper than 2H:1V that have not been stabilized
- Within natural water features if permitted
- Temporarily on banks of sediment control traps or basins
- Newly seeded areas if seeding does not provide immediate stabilization
- Erosion scars
|
RECP Installation Diagram
|
|
| Chemical Soil Stabilization
|
Substances that bind soil particles to stabilize the soil surface.
|
- Subject to CA approval within regulated area
- In conjunction with seeding in areas not accessed by vehicles
- Only applied on bare soil if: reapplied at recommended frequency, no concentrated flows, no vehicle traffic, short term use only
|
Anionic Polyacrylamide Application Guide for Urban Construction in Ontario (TRCA, 2013)
|
|
Sediment controls[edit]

Sediment fence posts should be no more than 2 m apart. Structural fencing support (page wire) or 10 by 10 wooden posts are preferred. The end runs of any perimeter controls should extend a sufficient distance up slope to prevent flow from going around the control measure.

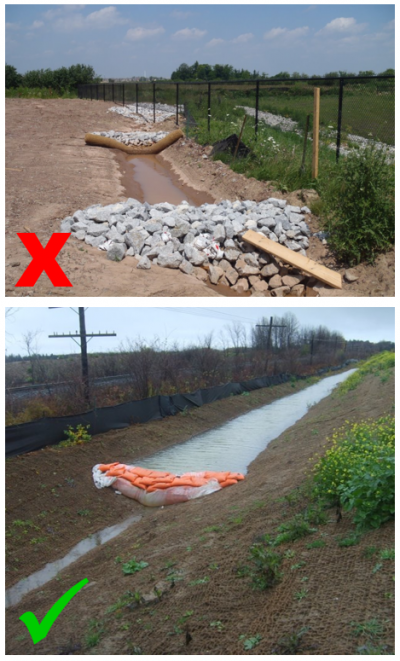
If a
sediment/dewatering bag is being used, ensure that it is in an appropriate location, changed when required, the area underneath is stabilized, and that there is a stable flow path from the bag to the receiver. Monitor to ensure discharge is clean and no erosion is occurring.
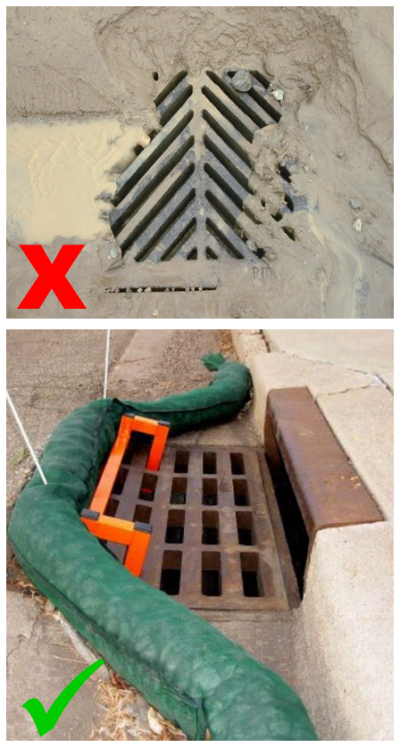

Protection, such as filter socks, should be installed around inlets. Filter socks should be staked whenever possible to prevent shifting, or reinforced with a board.
Table 2. Sediment controls
| BMP (click for more information)
|
Description
|
Applicability
|
Drawings and Additional Resources
|
Example Image
|
| Sediment Control Fence
|
Geotextile material supported by posts and trenched into the ground to support settling of sheet flows.
|
- Site perimeter
- up-gradient side of sensitive areas/streams
- Around material stockpiles
- 1.5 m away from slope base
- Do not install perpendicular to concentrated flows
- Parallel to areas with sediment laden sheet flow
|
Sediment control fence (unfrozen)
Sediment control fence (frozen)
|
|
| Filter Socks
|
Tubular mesh socks filled with wood chip or compost that dissipate flow velocities and pond water to promote sediment settling.
|
- applied along contours on level and sloped areas, perpendicular to sheet flows
- 1.5 m from slope base
- site perimeter
- as check dams in swales and ditches
- around storm drain inlets and sediment bags
- base of topsoil stockpiles
- in place of sediment fence when frozen
|
S2S Conference Presentation
Compost Biofilters for SWM (TRCA, 2007)
|
|
| Natural Fibre Logs
|
Similar to filter socks but made of biodegradable materials such as coir, straw, or wood.
|
- applied along contours on level and sloped areas, perpendicular to sheet flows
- 1.5 m from slope base
- site perimeter
- as check dams in swales and ditches
- Around storm drain inlets and sediment bags
- base of topsoil stockpiles
- in place of sediment fence when frozen
|
Coir log with stakes (Terrafix Geosynthetics, 2015)[4]
|
|
| Rock Check Dams
|
Weir constructed across channels from granular material and geotextile to reduce flow velocity.
|
- Perpendicular to concentrated flow channels, especially in long/steep channels
- Do not use in natural features
|
Temporary rock flow check dam diagram
|
|
| Vehicle Tracking Controls
|
Measures such as mud mats, shaker racks, or wheel washers to prevent vehicles from tracking mud offsite.
|
Vehicle tracking controls:
- site >1 ha
- grading/filling close to entrances
- Weather/site conditions cause mud
Wheel washing:
- Mud tracking ongoing issue and vehicle tracking controls not providing mitigation/cannot be constructed due to site constraints
- contaminated soils
- required by municipality
|
Mud mat
|
|
| Sediment Dewatering Bags
|
Large geotextile bags used to filter sediment-laden water from pumped discharge.
|
- anywhere dewatering necessary to create a dry work area, particularly where space limited
- where flow dispersion is needed to prevent erosion
- best used in treatment train
|
Dewatering treatment train (unfrozen)
Dewatering treatment train (frozen)
|
|
| Storm Drain Inlet Protection
|
Blocks sediment entry to inlets while allowing water through.
|
- all operational inlets at grade around or overtop the inlet
- below grade inside a storm drain
- treatment train required for drainage areas >1 ha
|
Excavated drop inlet
Gravel jacket
|
|
| Sediment Traps
|
Runoff detention area created by an embankment or depression to allow sediment settling.
|
- end of a treatment train before discharged offsite
- across drainage/conveyance features
- drainage areas ≤ 2 ha that do not drain to another detention feature
|
Sediment trap within an earthen ditch
|
|
| Sediment Ponds
|
Similar to sediment traps but larger. Excavated depression for permanent water retention.
|
- Treatment of runoff from drainage areas > 2 ha
- end-of-pipe control
|
Sediment control pond
STEP Wet Ponds Page
|
|
| Weir Tanks
|
Tanks that detain stormwater runoff to promote sediment settling.
|
- Sediment removal for short-term pumping / dewatering activities
- when more stringent effluent water quality standards required
- Planned pumping rates are high and require large capacity
|
|
|
| Polymer Flocculants
|
Chemical agents that bind suspended particles to enhance sediment removal.
|
- Treatment for short-term pumping activities
- A high sediment removal rate is required but area too small for wet pond
- Water contains contaminants or a large proportion of fine sediments
- more stringent effluent water quality standards required
- Other conventional BMPs cannot achieve removal rates
|
STEP polymers page
|
|
| Active Treatment Systems
|
Systems combining tanks, flocculants, and filters for precise and high-efficiency contaminant removal.
|
- Treatment for short-term pumping activities
- A high sediment removal rate is required but area too small for wet pond
- Water contains contaminants
- more stringent effluent water quality standards required
- Other conventional BMPs cannot achieve removal rates
|
|
|
Protecting LID features during construction[edit]
LID practices that promote infiltration as their primary function for water quality & management of overland flows, such as bioretention areas, permeable pavements, and infiltration trenches, are vulnerable to damage during construction activities that can compromise their ability to function as intended. These features can become clogged with sediment, experience erosion at inlets and in planted areas, suffer compaction from heavy machinery, or be contaminated by pollutants in construction runoff. To minimize these risks and maintain effective protection throughout all phases of construction, the following best practices should be implemented:
Keep LID perimeter controls in working order throughout construction. ESC measures at this bioretention feature were removed before construction in its drainage was complete, allowing sediment into it (Photo Source: CVC).
Avoid heavy equipment on infiltration areas (i.e., driving vehicles through filter beds, or over granular water storage and bedding layers). Identify and mark LID areas to increase awareness.
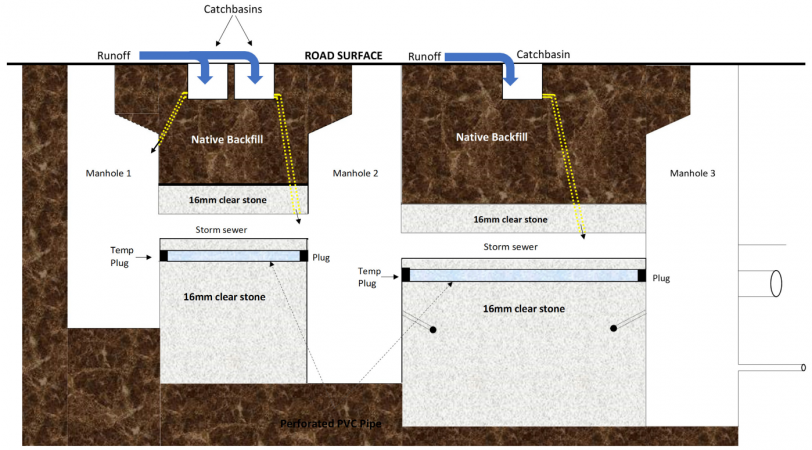
Phase construction so that LID measures are constructed last. Underground LID features can be built early in the construction process, provided they are protected by a barrier such as a plug. Graphic shows an exfiltration system with a temporary plug keeping construction runoff out of the exfiltration area.
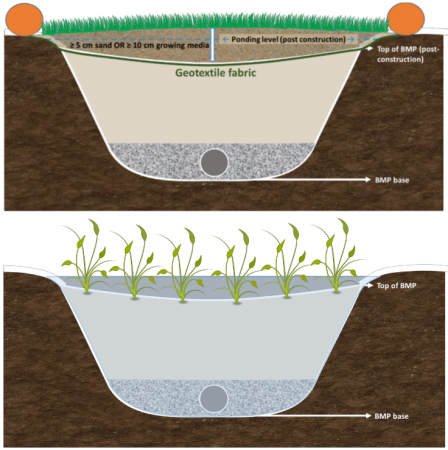
Keep LID installations offline via flow diversion until construction is complete, the drainage area is stabilized, and vehicle mud tracking is stopped. Image shows a bioretention feature during construction (left) and post-construction (right). The LID feature is protected using geotextile fabric, a sacrificial layer of stabilized sand/growing media with vegetation, and a filter sock. Once surrounding construction is complete, the layer of growing media is removed and the BMP starts receiving flow.
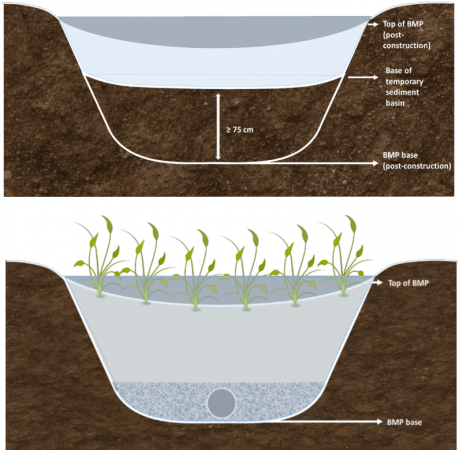
Avoid using LID areas as temporary detention basins, but in cases where flow cannot be routed around LID areas, protection should be used to prevent accumulated sediment from migrating into the subgrade. Graphic shows a bioretention feature during construction (left) and post-construction (right). At least 75 cm of native soil is retained between the base of the detention basin and the base of the LID feature, so that sediment accumulation in the detention basin can be removed. Once it is excavated and filled, ESC measures should be put in place to protect it until all drainage area construction and stabilization are complete.
Be mindful of stockpile locations relative to LID areas.
Inspect LID areas during ESC site inspections.
Spill response[edit]
Creating a spill response, control, and reporting plan is a key part of ESC for construction projects. Although spills are not common, their environmental impact can be significant. A well-developed plan allows for quick, effective action that reduces environmental harm and cleanup needs. It also shows due diligence in protecting natural features.
At a minimum, the plan should include:
- Emergency contact numbers;
- A list of on-site spill control materials; and
- Clear steps for responding to different types of spills.
Prevention is equally important and involves:
- Identifying potential pollutants;
- Assessing risks; and,
- Safely storing materials away from storm drains and water bodies.
When spills occur, immediate action is required. Minor spills must be contained, cleaned up, and documented. Significant spills, such as those that may affect nearby or downstream water features, must be reported right away to the contract administrator, Ontario Spills Action Centre, and other relevant contacts. Response efforts should begin immediately, including monitoring and recording spill details and cleanup steps. Strong planning, prevention, and response protocols help minimize environmental damage during construction.
An example spill response/reporting plan by the City of Mississauga for small, medium, and large spills is available for download (downward facing arrow on the top righthand side) and printing (printer emoticon on top right hand side) on the right.
Plan submission and approval[edit]
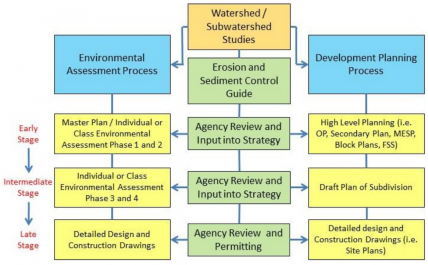
Flow chart showing the ESC plan approval process, divided into early, intermediate, and late stages.
The submission requirements for erosion and sediment control strategies are organized based on three planning stages: early, intermediate, and late, which align with both the land-use and infrastructure planning processes. Each stage builds on the previous one, helping to gradually refine ESC strategies as more project details become available.
- In the early stage, the focus is on high-level planning, identifying potential impacts, and committing to appropriate ESC approaches.
- During the intermediate stage, ESC planning becomes more site-specific, using detailed information about layout, grading, and servicing.
- In the late stage, a comprehensive ESC report and drawings are submitted.
This progressive approach ensures that ESC strategies evolve alongside the project’s design and that regulatory requirements are addressed at each stage. The permits and approvals required for an urban construction project are dictated by relevant legislation as well as project and site-specific circumstances. Early consultation with regulatory agencies is encouraged in order to allow time for any necessary permits and approvals to be issued. Refer to Chapters 8 and 9 in the Erosion and Sediment Control Guide for Urban Construction (2019) for full details on requirements for each planning stage and the approvals process.
For projects requiring a TRCA permit, information on the TRCA permitting process can be found here.
ESC report contents and drawings checklists, created by TRCA in 2019, are available for download here.
Routine inspection[edit]
ESC inspection programs regularly assess the effectiveness of BMPs, identify maintenance and repair needs, and identify areas where BMPs should be replaced or augmented. Consult the appendices linked in the first column of table 1 and 2 for BMP-specific inspection points.
Inspections should be conducted:
- Before there is any activity to see the natural landscape, drainage, and sensitive features
- During the initial installation of ESC measures
- On a weekly basis during active construction
- Before and after significant rainfall and snowmelt events
- After any extreme weather which could result in damage to ESC measures
- Daily during extended rain or snowmelt periods
- Monthly during inactive periods (> 30 days)
- During or immediately following any spill event
- Before construction is shut down for the winter to ensure the site is ready for freezing conditions and thaws
- At the end of construction to confirm that the site has achieved at least 80% stabilization and that permanent vegetation areas are well-established and effectively preventing erosion

Ponding in front of this
catchbasin indicates that this ESC inlet control is working. Ponding water allows for suspended
sediments to settle. (Photo source: CISEC)

This inlet control has worked well, but the
sediment should be removed as soon as possible. (Photo source: CISEC)
Where applicable, inspections of ESC measures should be integrated with inspections of LID features. Construction and assumption inspections for LID features are often required on the same schedule as ESC measures - for example, weekly, after major storm events, or at key construction milestones. You can download (downward facing arrow on the top righthand side) and print (printer emoticon on top right hand side) the inspection report template on the right.
Performance Monitoring[edit]
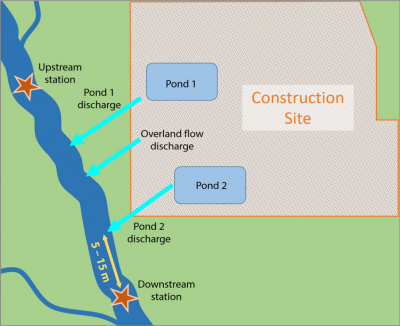
Map showing an example construction site with two
pond discharges and an upstream and downstream monitoring site.

An in-water turbidity monitoring station.
It is important to evaluate the cumulative effectiveness of all the controls installed on a construction site. Turbidity (a proxy for TSS) of the site discharges or the receiving water system is typically measured to assess ESC effectiveness. Turbidity targets vary based on duration of exposure, as the extent of potential harm to receiving aquatic ecosystems is dictated by both concentration and duration:
Table 3: Maximum allowable construction-based turbidity increases in the receiving water system at different durations
| Construction-based turbidity increase (NTU)
|
Duration (h)
|
| 761
|
0.5
|
| 324
|
1
|
| 138
|
2
|
| 84
|
3
|
| 59
|
4
|
| 45
|
5
|
| 36
|
6
|
| 29
|
7
|
| ≤ 25
|
Any duration
|
The extent of turbidity monitoring and methods used on a given construction project should be based on erosion risk, receiving water flows, presence of species at risk, and type and location of discharge points.
The monitoring program for sites applying the receiving water target should include the following components:
- One continuous online turbidity monitoring station 5 to 15 m downstream of the last site discharge point.
- At least one continuous online turbidity monitoring station immediately upstream of the site.
Each turbidity monitoring station should be equipped with a turbidity sonde, data logger, power supply, protective enclosure, and, where Species at Risk (SAR) are present, telemetry capabilities. Continuous turbidity monitoring should be maintained until the site has reached at least 80% effective permanent stabilization. Where continuous monitoring is not feasible, grab samples should be collected. To support interpretation of turbidity exceedances, precipitation data should be obtained from a rain gauge located within 5 km of the site. Clear protocols for responding to and reporting turbidity exceedances should be established for all sites with continuous monitoring.
Maintenance of ESC[edit]
Timely maintenance of ESC practices is essential for demonstrating due diligence on construction sites. Repairs or replacements should be completed promptly - within 48 h, or sooner if there is imminent environmental risk. Where feasible, backup materials should be stored on-site to expedite maintenance. Maintenance tasks vary depending on the ESC practice and a list of maintenance tasks can be found for each BMP by clicking on the first column of table 1 and 2. General ESC maintenance tasks are listed in Table 4.
Table 4. ESC maintenance and repair activities
| Category
|
Key Actions and Considerations
|
| Surface Repair
|
- Regrade and fill eroded areas
- Upgrade stabilization where existing measures are inadequate
- Ensure discharge points are not causing erosion and apply stabilization if needed
- Restore disturbed or compacted areas caused by vehicle or equipment access
|
| Sediment Removal
|
- Remove and dispose of accumulated sediment before capacity is exceeded or when clogged
- Rake or replace overloaded granular materials
|
| Structural Repair
|
- Repair or replace damaged components such as filter socks and silt fences
- Reposition or resecure devices that have shifted
- Reinforce access restrictions to protected or stabilized areas
|
| Vegetation Restoration
|
- Re-seed areas where vegetation has failed
- Repair or replace damaged tree protection fencing or buffer zones
|
| Flow Control Adjustments
|
- Modify or reinforce swales, slope drains, and energy dissipators where flows are causing erosion or bypass
- Add or upgrade flow interruption devices if current setups are overwhelmed
- Regrade swales or adjust flow paths to reduce velocity and erosion risk
|
| Corrective Actions
|
- Implement fixes for recurring failures
- Replace underperforming ESC measures with more effective alternatives where necessary
- Prioritize and complete urgent repairs
|
Decommissioning of ESC[edit]
Decommissioning practices vary depending on the ESC and specific considerations can be found for each BMP by clicking on the first column of table 1 and 2. General ESC decommissioning considerations are listed in Table 5.
Table 5. ESC decommissioning
| Category
|
Key Actions and Considerations
|
| Timing & Prerequisites
|
- Follow construction drawing sequencing, typically working upstream to downstream
- Only decommission ESC measures once areas receiving runoff are fully stabilized (i.e., vegetation well-established, slopes stabilized)
- Ensure runoff has been re-routed appropriately before removing conveyance features
|
| Sediment and Material Removal
|
- Remove accumulated sediment from ESC and dispose of in accordance with sediment quality and applicable legislation
- Treat water from dewatering activities using suitable sediment removal BMPs (e.g., sediment bags, weir tanks)
- Ensure flocculants and chemically treated sediment are disposed of properly
- Prevent thermal impacts by releasing water gradually to vegetated areas instead of directly into watercourses
|
| ESC Feature Removal
|
- Remove temporary ESC structures with minimal disturbance to stabilized areas and natural features
- Reusable materials (e.g., stakes, fence fabric) may be salvaged; others should be disposed of at appropriate facilities
- Biodegradable materials may be left in place if allowed and seeded appropriately for long-term restoration
- Some ESC practices may be retained or transitioned to permanent controls to manage long-term erosion and prevent sediment transport
|
| Site Stabilization & Restoration
|
- All disturbed areas must be graded and stabilized per final design
- Use native, weed-free vegetation for site restoration
- Stabilize areas before flow is returned to newly constructed or natural channels
|
| Regulatory Compliance
|
- Ensure removal follows manufacturer recommendations
- Coordinate with regulatory authorities where required
- Ensure stranded wildlife are safely relocated in accordance with permits
|
Additional Resources[edit]
References[edit]