Difference between revisions of "Bioretention: Partial infiltration"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <imagemap> | ||
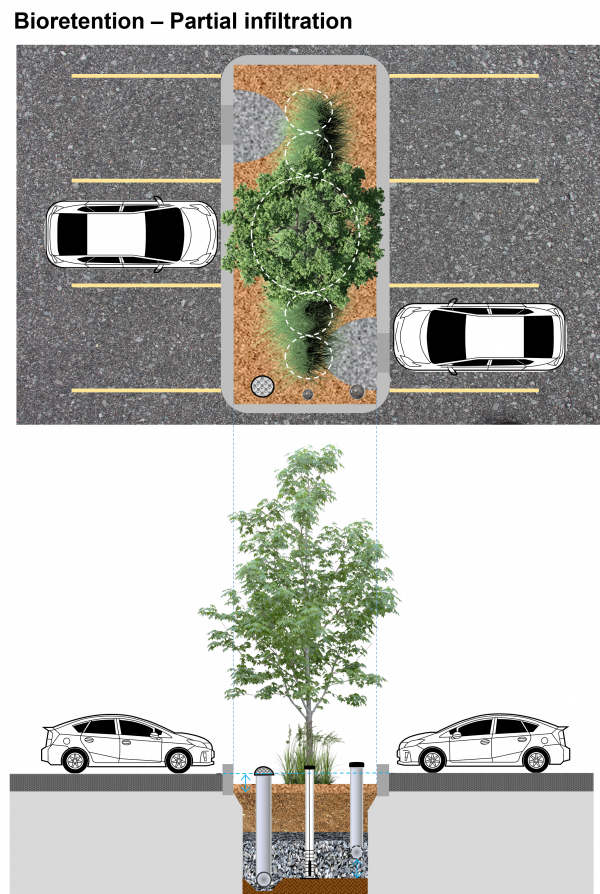
| + | File:Bioretention Full Partial infiltration placementswap.png|thumb|600px|'''Partial infiltration''' bioretention cell draining a parking lot. This design variation includes an underdrain and surface overflow pipes that allow excess water to leave the practice. A monitoring well is included so drainage performance can be evaluated over its operating lifespan. For more details on this variation of a bioretention feature and others, click here for the [https://www.toronto.ca/legdocs/mmis/2017/pw/bgrd/backgroundfile-107514.pdf City of Toronto's Green Streets Technical Guidelines (GSTG).],<ref>City of Toronto. 2017. City of Toronto's Green Streets Technical Guidelines - Version 1.0. Schollen & Company Inc., Urban Forest Innovators, TMIG, DMG. August, 2017. https://www.toronto.ca/legdocs/mmis/2017/pw/bgrd/backgroundfile-107514.pdf</ref> <span style="color:red">'''''Note''': The following is an "image map", feel free to explore the image with your cursor and click on highlighted labels that appear to take you to corresponding pages on the Wiki.''</span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | rect 1295 2828 1342 3128 [[Underdrains|Underdrain Access Structure]] | ||
| + | rect 1296 1423 1348 1478 [[Underdrains|Underdrain Access Structure]] | ||
| + | rect 1293 3128 1346 3178 [[Underdrains|Underdrain]] | ||
| + | rect 1134 3187 1159 3246 [[Digital technologies|Water Level Sensor]] | ||
| + | rect 1112 3181 1169 3250 [[Bioretention: Internal water storage|Internal Water Storage]] | ||
| + | rect 1126 2838 1163 3187 [[Wells|Monitoring Well]] | ||
| + | rect 1116 1437 1163 1480 [[Wells|Monitoring Well]] | ||
| + | rect 1295 3183 1348 3254 [[Bioretention: Internal water storage|Internal Water Storage]] | ||
| + | rect 939 1415 1011 1482 [[Overflow|Overflow Outlet]] | ||
| + | rect 956 2845 1017 3177 [[Overflow|Overflow Outlet]] | ||
| + | rect 935 3229 1012 3285 [[Overflow|Overflow Outlet Pipe]] | ||
| + | poly 866 326 866 241 1386 241 1386 416 1392 683 1337 620 1270 579 1278 410 1241 339 1078 326 1045 398 1049 400 992 355 [[Mulch|Mulch]] | ||
| + | poly 870 685 868 610 1000 567 1004 632 [[Mulch|Mulch]] | ||
| + | poly 868 1028 966 1081 1021 1370 864 1485 870 1283 868 1211 870 1136 [[Mulch|Mulch]] | ||
| + | poly 990 1397 1045 1482 1110 1485 1111 1421 [[Mulch|Mulch]] | ||
| + | poly 1214 1389 1263 1419 1339 1440 1390 1446 1384 1491 1161 1497 [[Mulch|Mulch]] | ||
| + | poly 1292 1062 1386 1032 1384 1164 1249 1209 [[Mulch|Mulch]] | ||
| + | rect 1027 379 870 575 [[Stone|Erosion Control - Stone]] | ||
| + | rect 1241 1223 1392 1432 [[Stone|Erosion Control - Stone]] | ||
| + | rect 815 389 868 540 [[Curb cuts|Curb Cut]] | ||
| + | rect 1398 1234 1441 1378 [[Curb cuts|Curb Cut]] | ||
| + | rect 862 685 1388 1038 [[Trees: List|Tree]] | ||
| + | rect 1068 351 1245 648 [[Plant lists|Vegetation]] | ||
| + | rect 1007 1089 1235 1399 [[Plant lists|Vegetation]] | ||
| + | rect 854 1652 1408 2651 [[Trees: List|Tree]] | ||
| + | rect 1064 2684 1227 2822 [[Plant lists|Vegetation]] | ||
| + | rect 862 2863 955 2940 [[Flow through media|Ponding Depth]] | ||
| + | rect 1017 2902 1119 2942 [[Mulch|Mulch]] | ||
| + | rect 1164 2900 1398 2938 [[Mulch|Mulch]] | ||
| + | rect 864 2943 955 3079 [[Bioretention: Filter media|Filter Media]] | ||
| + | rect 1023 2941 1111 3083 [[Bioretention: Filter media|Filter Media]] | ||
| + | rect 1168 2938 1392 3081 [[Bioretention: Filter media|Filter Media]] | ||
| + | rect 866 3083 953 3116 [[Choker layer|Choker Layer]] | ||
| + | rect 1021 3079 1110 3116 [[Choker layer|Choker Layer]] | ||
| + | rect 1168 3085 1386 3116 [[Choker layer|Choker Layer]] | ||
| + | rect 868 3120 955 3185 [[Reservoir aggregate|Clear Stone / Aggregate]] | ||
| + | rect 1023 3114 1113 3189 [[Reservoir aggregate|Clear Stone / Aggregate]] | ||
| + | rect 1170 3116 1388 3191 [[Reservoir aggregate|Clear Stone / Aggregate]] | ||
| + | rect 1045 3252 1363 3309 [[Soil Groups|Compacted Subgrade Soil]] | ||
| + | rect 900 3289 1047 3309 [[Soil Groups|Compacted Subgrade Soil]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | </imagemap> | ||
| + | |||
<div class="col-md-8"> | <div class="col-md-8"> | ||
| − | + | {{TOClimit|2}} | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ==Overview== | ||
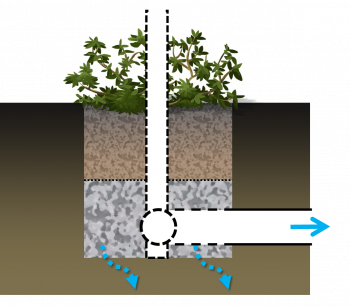
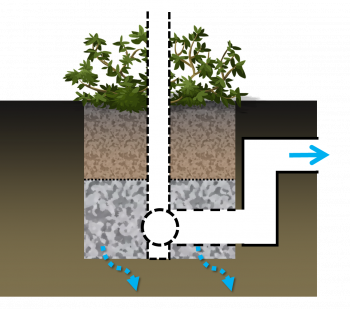
| + | Over soils with slow infiltration rates, it is advantageous to drain a portion of the stored water prior to any upcoming storm. This popular design choice can optimize annual water balance, mitigate peak flow rates and by ensuring water flow through, can reduce the accumulation of sodium and chlorine ions from winter salting. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Partial infiltration.png|350px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Partially infiltrating bioretention with underdrain. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File: Partial with storage.png|350px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Partially infiltrating bioretention with anaerobic/aerobic storage zone. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Materials== | ||
| + | *[[Underdrain]] | ||
| + | *[[Biomedia]] | ||
| + | *[[Erosion control blankets|Erosion control]] | ||
| + | *[[Mulch]] | ||
| + | *[[Planting design|Planting considerations]] and [[Plant lists| Recommended species]] | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | {{Clickable button|[[Bioretention cells|Back to Bioretention]]}} | |
| − | === | + | ==References== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[category: Infiltration]] | |
| − | [[category:Infiltration]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:25, 27 September 2022

Partial infiltration bioretention cell draining a parking lot. This design variation includes an underdrain and surface overflow pipes that allow excess water to leave the practice. A monitoring well is included so drainage performance can be evaluated over its operating lifespan. For more details on this variation of a bioretention feature and others, click here for the City of Toronto's Green Streets Technical Guidelines (GSTG).,[1] Note: The following is an "image map", feel free to explore the image with your cursor and click on highlighted labels that appear to take you to corresponding pages on the Wiki.
Overview[edit]
Over soils with slow infiltration rates, it is advantageous to drain a portion of the stored water prior to any upcoming storm. This popular design choice can optimize annual water balance, mitigate peak flow rates and by ensuring water flow through, can reduce the accumulation of sodium and chlorine ions from winter salting.
Partially infiltrating bioretention with underdrain.
Partially infiltrating bioretention with anaerobic/aerobic storage zone.
Materials[edit]
References[edit]
- ↑ City of Toronto. 2017. City of Toronto's Green Streets Technical Guidelines - Version 1.0. Schollen & Company Inc., Urban Forest Innovators, TMIG, DMG. August, 2017. https://www.toronto.ca/legdocs/mmis/2017/pw/bgrd/backgroundfile-107514.pdf