Difference between revisions of "Planters: Sizing"
Dean Young (talk | contribs) |
Dean Young (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
* 0.35 for more loamy Blend B - Water quality treatment priority | * 0.35 for more loamy Blend B - Water quality treatment priority | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Choker layer |
| − | | | + | | 100 mm |
| + | | 0.4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Perforated pipe diameter | ||
| + | | 150 to 200 mm | ||
| 0.4 | | 0.4 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Clear stone aggregate layer below perforated pipe |
| 50 mm (although commonly omitted altogether). | | 50 mm (although commonly omitted altogether). | ||
| 0.4 | | 0.4 | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 22:26, 20 May 2022
This article is specific to flow-through stormwater planters, vegetated systems that do not infiltrate water to the native soil.
If you are designing a planted system which does infiltrate water, see advice on Bioretention: Sizing.
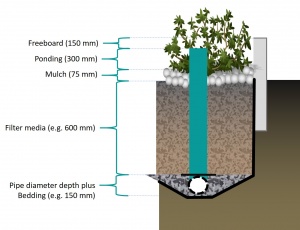
The dimensions of a stormwater planter are largely predetermined according to the function of the component. As they do not contain a storage reservoir the planters rely more upon careful selection of materials. Both the saturated hydraulic conductivity of the filter media and the number and size of perforations of the underdrain pipe play critical roles for flow control. Options for maintaining separation between filter media and clear stone aggregate surrounding the perforated pipe include a 100 mm deep choker layer or sheet of geotextile filter fabric.
| Component | Recommended depth (with underdrain pipe) | Typical porosity (n) |
|---|---|---|
| Ponding (dp) | 150 to 450 mm | 1 |
| Mulch | 75 ± 25 mm |
|
| Filter media (dm) |
|
|
| Choker layer | 100 mm | 0.4 |
| Perforated pipe diameter | 150 to 200 mm | 0.4 |
| Clear stone aggregate layer below perforated pipe | 50 mm (although commonly omitted altogether). | 0.4 |