Grading
Expressing slope[edit]
Slope gradient[edit]
Slope gradients are are common form of expression for steeply sloped areas like the sides of swales. Expressed as Y:X where Y is a single unit of rise and X is the corresponding run. It can be calculated by dividing the rise by the run: e.g.:
Slope percentage[edit]
Slope percentage is calculated similarly by dividing rise by run, but then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage: e.g.: But for many calculations the rise/run isn't multiplied by 100, and instead is left as a decimal. e.g. 0.33 in the example above.
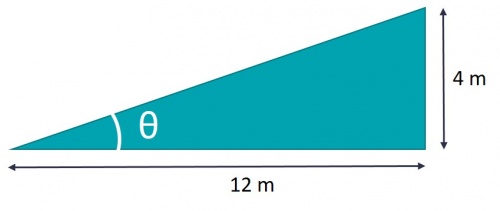
Slope in degrees[edit]
Expressing a slope in degrees requires using the tangent trigonometric function. e.g.:
Normal range of slopes[edit]
The Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act[1] provides a bare minimum to which public spaces must be designed. e.g. cross slope not to exceed 2 %.
Consider designing landscapes to universal design principals instead[2][3].
| Use | Extreme range (%) | Desirable range (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Public Streets | 0.5 - 10 | 1 - 8 |
| Private streets | 0.5 - 20 | 1 - 12 |
| Service lanes | 0.5 - 15 | 1 - 10 |
| Parking areas | 0.5 - 8 | 1 - 5 |
| Parking ramps | up to 20 | up to 15 |
| Collector walks | 0.5 - 12 | 1 - 8 |
| Entrance walks | 0.5 - 8 | 1 - 4 |
| Pedestrian ramps | up to 12 | up to 8 |
| Stairs | 25 - 50 | 33 - 50 |
| Game courts | 0.5 - 2 | 0.5 - 1.5 |
| Paved gutters | 0.25 - 100 | 1 - 50 |
| Grassed swales | 0.5 - 15 | 2 - 10 |
| Terraces and sitting areas | 0.5 - 3 | 1 - 2 |
| Grassed banks | up to 50 | up to 33 |
| Planted banks | up to 100 | up to 50 |
Freeboard[edit]
- In swales conveying flowing water a freeboard of 300 mm is generally accepted as a good starting point.
- In bioretention the freeboard is the difference between the invert elevation of the inlet and overflow structure. 150 mm will usually suffice, so long as the inlet will not become inundated during design storm conditions.
- In above grade stormwater planters, the equivalent dimension would be the difference between the invert elevation of the lip of the planter and the overflow structure (150 mm minimum).
Additional Resources[edit]
- Planning and Design (Huang, 2012)[5]
- Grading and Earthwork (Matusik and Deibel, 2004)[6]
- Fundamentals of Site Grading Design (Tiner, 2014)[7]
- Slope-Meter, Inc. - external resource, Slope Conversion Table (Slope-Meter Inc. 2009)[8]
References[edit]
- ↑ Ontario. O. Reg. 191/11: INTEGRATED ACCESSIBILITY STANDARDS, 2011. https://www.ontario.ca/laws/regulation/r11191.
- ↑ Universal Design.com. 2018. “The Leading Source for News and Information on Universal Design - The Leading Source for News and Information on Universal Design.” 2018. http://www.universaldesign.com/.
- ↑ Institute for Human Centered Design. 2018. “Principles.” 2018. https://www.humancentereddesign.org/inclusive-design/principles.
- ↑ Strom, S., Nathan, K., Woland, J. Site Engineering for Landscape Architects (6th Ed.) 2013, Wiley and Sons
- ↑ Huang, J. C. 2012. PDH online Course C115 (5 PDH) - Site Planning and Design. UNIFIED FACILITIES CRITERIA (UFC) SITE PLANNING AND DESIGN. U.S department of Defense. https://wiki.sustainabletechnologies.ca/images/3/39/Huang_2012.pdf
- ↑ Matusik, J., and Deibel, D. 2004. Land Development Handbook - CHAPTER 24: Grading and Earthwork. Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com). https://wikidev.sustainabletechnologies.ca/images/d/d7/Matusik_2004.pdf
- ↑ Tiner, J. A. 2014. Fundamentals of Site Grading Design. A SunCam online continuing education course. https://wiki.sustainabletechnologies.ca/images/a/a5/Tiner_2014.pdf
- ↑ Slope-Meter Inc. 2009. Download Slope Conversion Tables. Copyright 2009 - Slope-Meter Inc. - All Rights Reserved. http://slopemeter.com/images/Slope_Conversion_Tables.xls