Difference between revisions of "Bioretention: Partial infiltration"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) |
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Performance== | ==Performance== | ||
{{:Bioretention: Water quality}} | {{:Bioretention: Water quality}} | ||
| − | ==Materials | + | ==Materials== |
*[[Underdrain]] | *[[Underdrain]] | ||
*[[Biomedia]] | *[[Biomedia]] | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
*[[Mulch|Mulch]] | *[[Mulch|Mulch]] | ||
*[[Bioretention: Planting plans|Planting considerations]] and [[Bioretention: Plant list| Recommended species]] | *[[Bioretention: Planting plans|Planting considerations]] and [[Bioretention: Plant list| Recommended species]] | ||
| + | |||
==Research== | ==Research== | ||
{{:Bioretention:_Partial_infiltration_volume}} | {{:Bioretention:_Partial_infiltration_volume}} | ||
Revision as of 01:32, 8 September 2017
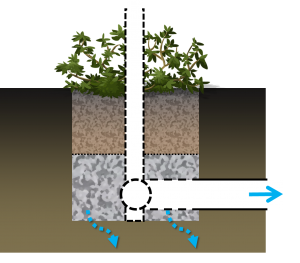
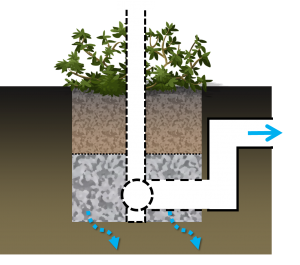
Overview[edit]
Over soils with slow infiltration rates, it is advantageous to drain a portion of the stored water prior to any upcoming storm. This popular design choice can optimize annual water balance, mitigate peak flow rates and by ensuring water flow through, can reduce the accumulation of sodium and chlorine ions from winter salting.