Difference between revisions of "Rainwater harvesting: Sizing and modeling"
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) (→Simple) |
|||
| (71 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
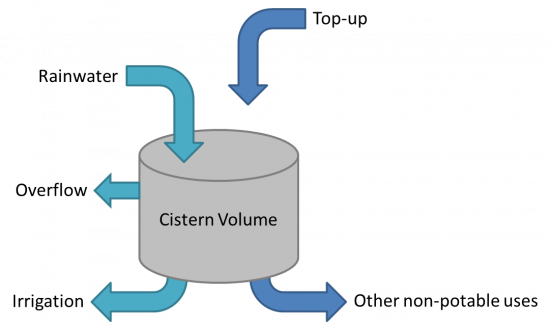
| − | + | [[File:Cistern Size.png|thumb|550px|Schematic diagram of the inputs and outputs to a rainwater harvesting cistern]] | |
| − | + | {{TOClimit}} | |
| − | [[File:Cistern Size.png|thumb|Schematic diagram of the inputs and outputs to a rainwater harvesting cistern]] | + | |
===Simple=== | ===Simple=== | ||
| − | + | The following approximations | |
| − | + | Five percent of the average annual yield can be estimated: | |
| − | + | <math>Y_{0.05} = A_{c} \times C_{vol,A}\times R_{a} \times e \times 0.05</math> | |
| − | * | + | {{plainlist|Where: |
| − | *A | + | *''Y<sub>0.05</sub>'' is five percent of the average annual yield (L) |
| − | *C<sub>vol, | + | *''A<sub>c</sub>'' is the catchment area (m<sup>2</sup>) |
| − | *R<sub> | + | *''C<sub>vol, A</sub>'' is the annual runoff coefficient for the catchment |
| − | *e | + | *''R<sub>a</sub>'' is the average annual rainfall depth (mm) |
| + | *''e'' is the efficiency of the pre-storage filter}} | ||
| + | *Filter efficiency (''e'') can be reasonably estimated as 0.9 pending manufacturer’s information.<br> | ||
| + | *In a study of three sites in Ontario, STEP found the annual ''C<sub>vol, A</sub>'' of the rooftops to be around 0.8 [http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/home/urban-runoff-green-infrastructure/low-impact-development/rainwater-harvesting/performance-evaluation-of-rainwater-harvesting-systems-toronto-ontario/]. This figure includes losses to evaporation, snow being blown off the roof, and a number of overflow events. | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | Five percent of the average annual demand can be estimated: | ||
| + | <math>D_{0.05} = P_{d} \times n\times 18.25</math> | ||
| + | {{plainlist|Where: | ||
| + | *''D<sub>0.05</sub>'' is five percent of the average annual demand (L) | ||
| + | *''P<sub>d</sub>'' is the daily demand per person (L) | ||
| + | *''n'' is the number of occupants}} | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | Then the following calculations are based upon two criteria: | ||
| + | # A design rainfall depth is to be captured entirely by the RWH system. | ||
| + | # The average annual demand (''D'') is greater than the average annual yield (''Y'') from the catchment. | ||
| + | When \(Y_{0.05}/D_{0.05}<0.33\), the storage volume required can be estimated: | ||
| + | <math>V_{S} = A_{c} \times C_{vol,E}\times R_{d} \times e</math> | ||
| + | {{plainlist|Where: | ||
| + | *''V<sub>S</sub>'' is the volume of storage required (L) | ||
| + | *''A<sub>c</sub>'' is the catchment area (m<sup>2</sup>) | ||
| + | *''C<sub>vol,E</sub>'' is the design storm runoff coefficient for the catchment | ||
| + | *''R<sub>d</sub>'' is the design storm rainfall depth (mm), and | ||
| + | *''e'' is the efficiency of the pre-storage filter.}} | ||
| − | + | *Careful catchment selection means that the runoff coefficient, for an individual rainstorm event (''C<sub>vol, E</sub>'') should be 0.9 or greater. | |
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | + | Finally, when \(0.33<Y_{0.05}/D_{0.05}<0.7\), the total storage required can be estimated by adding ''Y<sub>0.05</sub>'': | |
| − | + | <math>TotalStorage = V_{S} + Y_{0.05}</math> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | < | ||
| − | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| + | ==STEP Rainwater Harvesting Tool== | ||
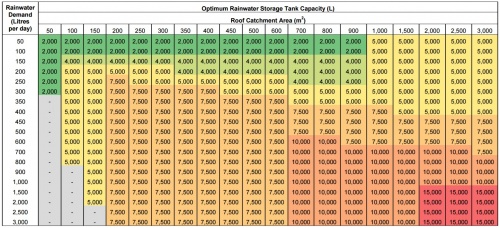
| + | [[File:RWH_tank_capacity_table.jpg|thumb|500 px|Quick reference table generated using STEP RWH tool, (data for the City of Toronto (median annual rainfall 678 mm). Optimal cistern size is that providing at least a 2.5% improvement in water savings following an increase of 1,000 Litres in storage capacity.]] | ||
| + | The Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program have produced a rainwater harvesting design and costing tool specific to Ontario. The tool is in a simple to use Excel format and is free to download.<br> | ||
| + | {{clickable button|[[File:Connect the Drops.PNG|200 px|link=http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/home/urban-runoff-green-infrastructure/low-impact-development/rainwater-harvesting/rainwater-harvesting-design-and-costing-tool/]]}} | ||
| − | + | ==STEP Treatment Train Tool== | |
| − | [[File: | + | {{Clickable button|[[File:TTT.png|300 px|link=http://www.sustainabletechnologies.ca/wp/low-impact-development-treatment-train-tool/]]}}<br> |
| − | + | '''[[Rainwater harvesting: TTT]]''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Cistern dimensions== |
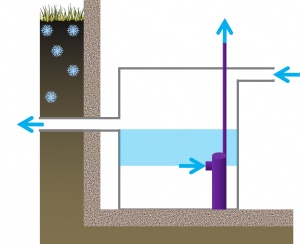
| − | + | [[File:Cistern dimensions.jpg|thumb|The blue area indicates the only usable volume in this rainwater harvesting cistern, the depth between the pump inlet and the overflow.]] | |
| − | + | The connections into and out of a rainwater cistern can have a dramatic effect on the actual usable volume. The only usable water within the cistern is that above the height of the pump intake, and below the invert of the overflow outlet. This dimension can easily become constrained where the outlet must lie beneath the frost line and where a high powered pump is required to elevate the water many storeys. | |
| − | + | * The depth of storage between the elevation of the inlet and overflow is unusable space, so the overflow should be located towards the top of the cistern. | |
| − | + | * The depth of storage beneath the pump inlet is unusable, but may also be a useful zone for sediment to settle. A custom or cast-in-place vault could minimise this unused volume by tapering towards the the base. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | *The | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[category:modeling]] | [[category:modeling]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:16, 26 October 2023
Simple[edit]
The following approximations Five percent of the average annual yield can be estimated:
Where:
- Y0.05 is five percent of the average annual yield (L)
- Ac is the catchment area (m2)
- Cvol, A is the annual runoff coefficient for the catchment
- Ra is the average annual rainfall depth (mm)
- e is the efficiency of the pre-storage filter
- Filter efficiency (e) can be reasonably estimated as 0.9 pending manufacturer’s information.
- In a study of three sites in Ontario, STEP found the annual Cvol, A of the rooftops to be around 0.8 [1]. This figure includes losses to evaporation, snow being blown off the roof, and a number of overflow events.
Five percent of the average annual demand can be estimated:
Where:
- D0.05 is five percent of the average annual demand (L)
- Pd is the daily demand per person (L)
- n is the number of occupants
Then the following calculations are based upon two criteria:
- A design rainfall depth is to be captured entirely by the RWH system.
- The average annual demand (D) is greater than the average annual yield (Y) from the catchment.
When \(Y_{0.05}/D_{0.05}<0.33\), the storage volume required can be estimated:
Where:
- VS is the volume of storage required (L)
- Ac is the catchment area (m2)
- Cvol,E is the design storm runoff coefficient for the catchment
- Rd is the design storm rainfall depth (mm), and
- e is the efficiency of the pre-storage filter.
- Careful catchment selection means that the runoff coefficient, for an individual rainstorm event (Cvol, E) should be 0.9 or greater.
Finally, when \(0.33<Y_{0.05}/D_{0.05}<0.7\), the total storage required can be estimated by adding Y0.05:
STEP Rainwater Harvesting Tool[edit]
The Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program have produced a rainwater harvesting design and costing tool specific to Ontario. The tool is in a simple to use Excel format and is free to download.
STEP Treatment Train Tool[edit]
Cistern dimensions[edit]
The connections into and out of a rainwater cistern can have a dramatic effect on the actual usable volume. The only usable water within the cistern is that above the height of the pump intake, and below the invert of the overflow outlet. This dimension can easily become constrained where the outlet must lie beneath the frost line and where a high powered pump is required to elevate the water many storeys.
- The depth of storage between the elevation of the inlet and overflow is unusable space, so the overflow should be located towards the top of the cistern.
- The depth of storage beneath the pump inlet is unusable, but may also be a useful zone for sediment to settle. A custom or cast-in-place vault could minimise this unused volume by tapering towards the the base.