Difference between revisions of "Pipes"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) m |
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) m |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Pipes should have been manufactured in conformity with the latest standards by the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) or ASTM International. | Pipes should have been manufactured in conformity with the latest standards by the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) or ASTM International. | ||
| − | *Perforated pipes should be continuously perforated, smooth interior HDPE (or equivalent material) with a minimum inside diameter of 100 mm. | + | *Perforated pipes should be continuously perforated, smooth interior HDPE (or equivalent material) with a minimum inside diameter of 100 mm. |
| − | **Where freezing is a concern, horizontal underdrain pipes should be over-sized to a minimum 200 mm diameter. | + | **Smooth interior facilitates inspection and maintenance activities; internal corrugations can cause cameras or hydrojetting apparatus to become snagged. |
| − | + | *Where freezing is a concern, horizontal underdrain pipes should be over-sized to a minimum 200 mm diameter. | |
| − | + | *Perforations should be made on all sides of the pipe and provide a ≥ 1 m<sup>2</sup> of open area per linear meter of pipe. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*Non-perforated pipes should be used for conveyance to and away from the facility, including overflow. | *Non-perforated pipes should be used for conveyance to and away from the facility, including overflow. | ||
| − | * | + | *a perforated pipe with many rectangular slots has better drainage characteristics than a pipe with similar open area provided by fewer circular holes <ref>Hazenberg, G., and U. S. Panu (1991), Theoretical analysis of flow rate into perforated drain tubes, Water Resour. Res., 27(7), 1411–1418, doi:10.1029/91WR00779.</ref>. |
| + | ---- | ||
[[Category:Materials]] | [[Category:Materials]] | ||
Revision as of 23:26, 2 March 2018
Pipes should have been manufactured in conformity with the latest standards by the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) or ASTM International.
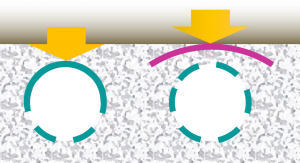
- Perforated pipes should be continuously perforated, smooth interior HDPE (or equivalent material) with a minimum inside diameter of 100 mm.
- Smooth interior facilitates inspection and maintenance activities; internal corrugations can cause cameras or hydrojetting apparatus to become snagged.
- Where freezing is a concern, horizontal underdrain pipes should be over-sized to a minimum 200 mm diameter.
- Perforations should be made on all sides of the pipe and provide a ≥ 1 m2 of open area per linear meter of pipe.
- Non-perforated pipes should be used for conveyance to and away from the facility, including overflow.
- a perforated pipe with many rectangular slots has better drainage characteristics than a pipe with similar open area provided by fewer circular holes [1].
- ↑ Hazenberg, G., and U. S. Panu (1991), Theoretical analysis of flow rate into perforated drain tubes, Water Resour. Res., 27(7), 1411–1418, doi:10.1029/91WR00779.