Difference between revisions of "Erosion and Sediment Control"
ChristineLN (talk | contribs) |
ChristineLN (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| − | =Overview= | + | ==Overview== |
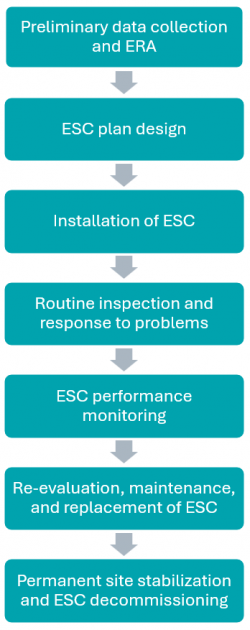
[[File:Screenshot 2025-07-29 102005.png|250px|thumb|right|Effective ESC starts before topsoil stripping begins. This flow chart shows the ESC process from construction project start to finish. Scroll through the wiki to read about each step of the process.]] | [[File:Screenshot 2025-07-29 102005.png|250px|thumb|right|Effective ESC starts before topsoil stripping begins. This flow chart shows the ESC process from construction project start to finish. Scroll through the wiki to read about each step of the process.]] | ||
Erosion and sediment controls (ESC) are technologies, practices and procedures that are applied to prevent the release of sediment from construction sites. | Erosion and sediment controls (ESC) are technologies, practices and procedures that are applied to prevent the release of sediment from construction sites. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
<br clear="all" /> | <br clear="all" /> | ||
| − | =Erosion risk assessments (ERA)= | + | ==Erosion risk assessments (ERA)== |
To manage the potential negative impacts of construction activities in the absence of effective ESC measures, Erosion Risk Assessments (ERAs) are conducted to guide the selection and placement of appropriate ESC practices on site. ERAs are recommended when: | To manage the potential negative impacts of construction activities in the absence of effective ESC measures, Erosion Risk Assessments (ERAs) are conducted to guide the selection and placement of appropriate ESC practices on site. ERAs are recommended when: | ||
{{textbox|*the extent of land disturbance is greater than 10 ha and duration is longer than 30 days, or | {{textbox|*the extent of land disturbance is greater than 10 ha and duration is longer than 30 days, or | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
The hybrid qualitative ERA approach is recommended in the above situations with the exception of instances where local regulatory agencies require a different approach. The hybrid qualitative ERA approach estimates erosion risk by dividing a site into areas based on soil, slope, and ground cover, then rating each area as low, moderate, or high erosion risk (link erosion potential subsection) to help choose the right erosion control practices for each stage of construction. | The hybrid qualitative ERA approach is recommended in the above situations with the exception of instances where local regulatory agencies require a different approach. The hybrid qualitative ERA approach estimates erosion risk by dividing a site into areas based on soil, slope, and ground cover, then rating each area as low, moderate, or high erosion risk (link erosion potential subsection) to help choose the right erosion control practices for each stage of construction. | ||
| − | =ESC plan design= | + | ==ESC plan design== |
An ESC plan should be created based on a given site’s ERA, with more controls used in the higher risk areas. An ESC plan should be designed for each stage of construction: | An ESC plan should be created based on a given site’s ERA, with more controls used in the higher risk areas. An ESC plan should be designed for each stage of construction: | ||
{{textbox|#Topsoil stripping, and re-stabilization | {{textbox|#Topsoil stripping, and re-stabilization | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
#Final stabilization/rehabilitation and ESC decommissioning}} | #Final stabilization/rehabilitation and ESC decommissioning}} | ||
| − | ==Types of ESC== | + | ===Types of ESC=== |
{{textbox|*Erosion controls prevent exposed soils from being entrained by water or wind. Practices that prevent erosion are the most effective BMPs because they address sediment at its source. | {{textbox|*Erosion controls prevent exposed soils from being entrained by water or wind. Practices that prevent erosion are the most effective BMPs because they address sediment at its source. | ||
*Sediment controls address the removal of sediment suspended in stormwater (reactive) through settling (link sedimentation page) and filtration (link filtration page).}} | *Sediment controls address the removal of sediment suspended in stormwater (reactive) through settling (link sedimentation page) and filtration (link filtration page).}} | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
The tables below provide an overview of common ESC BMPs. Click on the BMP name in the first column to read the detailed design requirements and installation, inspection, maintenance, and decommissioning guidance from https://sustainabletechnologies.ca/app/uploads/2020/01/ESC-Guide-for-Urban-Construction_FINAL.pdf. A description and common applications of each practice are listed in the second and third columns, respectively. The fourth column provides links to design drawings and other resources. | The tables below provide an overview of common ESC BMPs. Click on the BMP name in the first column to read the detailed design requirements and installation, inspection, maintenance, and decommissioning guidance from https://sustainabletechnologies.ca/app/uploads/2020/01/ESC-Guide-for-Urban-Construction_FINAL.pdf. A description and common applications of each practice are listed in the second and third columns, respectively. The fourth column provides links to design drawings and other resources. | ||
| − | ===Erosion controls=== | + | ====Erosion controls==== |
{| class="wikitable" style="width:100%; text-align:left;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:100%; text-align:left;" | ||
|+Table 1. Erosion Controls | |+Table 1. Erosion Controls | ||
| Line 148: | Line 148: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ===Sediment controls=== | + | ====Sediment controls==== |
{| class="wikitable" style="width:100%; text-align:left;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:100%; text-align:left;" | ||
|+Table 2. Sediment Controls | |+Table 2. Sediment Controls | ||
Revision as of 16:07, 7 November 2025
Note: This page is currently under revision.
Overview[edit]
Erosion and sediment controls (ESC) are technologies, practices and procedures that are applied to prevent the release of sediment from construction sites. Rapid urban expansion and associated construction activities are a significant source of stress to the natural environment. As construction processes involve the removal of vegetation and de-stabilization of soils, they can accelerate natural processes of erosion and sedimentation, mobilizing more sediment and associated contaminants that can ultimately end up in downstream receiving water systems. Erosion and Sediment Control (ESC) measures are essential to help reduce these sediment loads from active construction sites and protect downstream aquatic habitats from becoming impaired.
Inadequate ESC during construction can cause:
- sediment-laden runoff to enter downstream and adjacent natural features, including streams, lakes, wetlands and woodlots;
- deposition of sediment on adjacent private property and roadways;
- clogging of onsite stormwater management systems and LIDs;
- expensive cleanup and restoration costs;
- delays or stop-work orders; and
- fines from regulatory agencies.
Implementing effective ESC practices throughout all stages of construction is essential to sustainable urban growth and ensuring regulatory compliance.

Erosion risk assessments (ERA)[edit]
To manage the potential negative impacts of construction activities in the absence of effective ESC measures, Erosion Risk Assessments (ERAs) are conducted to guide the selection and placement of appropriate ESC practices on site. ERAs are recommended when:
- the extent of land disturbance is greater than 10 ha and duration is longer than 30 days, or
- construction activities are planned in or near natural water features, or
- the site drains to species at risk (SAR) habitat
The hybrid qualitative ERA approach is recommended in the above situations with the exception of instances where local regulatory agencies require a different approach. The hybrid qualitative ERA approach estimates erosion risk by dividing a site into areas based on soil, slope, and ground cover, then rating each area as low, moderate, or high erosion risk (link erosion potential subsection) to help choose the right erosion control practices for each stage of construction.
ESC plan design[edit]
An ESC plan should be created based on a given site’s ERA, with more controls used in the higher risk areas. An ESC plan should be designed for each stage of construction:
- Topsoil stripping, and re-stabilization
- Servicing
- Building construction
- Final stabilization/rehabilitation and ESC decommissioning
Types of ESC[edit]
- Erosion controls prevent exposed soils from being entrained by water or wind. Practices that prevent erosion are the most effective BMPs because they address sediment at its source.
- Sediment controls address the removal of sediment suspended in stormwater (reactive) through settling (link sedimentation page) and filtration (link filtration page).
The most effective way to apply ESC is to use a multi-barrier approach, which involves the installation of both types of controls in series, to create a resilient system capable of protecting the natural environment from sediment impacts. In a multi-barrier system there is redundancy so that if one control fails, there are still others in place to safeguard downstream features. Selecting the appropriate BMPs for each project stage requires an understanding of BMP function, intended use, expected performance, and maintenance required.
(Note: Isolation measures are not covered on this page but are detailed in the 2019 guide.) as side panel text box
The tables below provide an overview of common ESC BMPs. Click on the BMP name in the first column to read the detailed design requirements and installation, inspection, maintenance, and decommissioning guidance from https://sustainabletechnologies.ca/app/uploads/2020/01/ESC-Guide-for-Urban-Construction_FINAL.pdf. A description and common applications of each practice are listed in the second and third columns, respectively. The fourth column provides links to design drawings and other resources.
Erosion controls[edit]
| Practice (click for detailed design requirements – opens appendix PDF) | Description | Applicability | Design Drawings and Other Resources | Example Image (click to expand) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimized or Phased Land Clearing | Preservation of vegetated areas intercepts and infiltrates rainfall. | Areas not being immediately developed on larger sites (>10 ha) | ||
| Vegetated Filter Strips | Gently sloping, vegetated areas that slow and filter runoff. | Areas that may benefit from leaving vegetation in place | ||
| Slope Drains | Flexible pipe that conveys water down a disturbed slope to prevent erosion from concentrated runoff. | Exposed (and especially long or steep) slopes that convey concentrated flow | ||
| Interceptor Swales | Stabilized flow path that conveys runoff away from bare soil to sediment control measures. | Any unstabilized areas, but especially where:
|
||
| Outlet Protection | Energy dissipation devices or surface hardening that prevents scour erosion at outlets. | Base of any outlet releasing concentrated flow | ||
| Mulching | Layer of organic material (e.g., straw, bark, wood shavings, paper fibre, compost) that absorbs rainfall and acts as a physical barrier to erosion. |
|
||
| Seeding | Application of seed to establish vegetation for soil stability. | |||
| Surface Roughening | Creates uneven surfaces and depressions to reduce runoff velocity, trap sediment, keep seed in place, and improve vegetation establishment | *Inactive (<30 days) disturbed surfaces
|
||
| Rolled Erosion Control Products | Netting, blankets, or turf reinforcement mats act as a physical barrier to erosion. Biodegradable options free of plastic netting prevent wildlife ensnaring. | *Bare areas that convey concentrated flows
|
||
| Chemical Soil Stabilization | Substances that bind soil particles to stabilize the soil surface. |
|
Sediment controls[edit]
| Practice (click for detailed design requirements – opens appendix PDF) | Description | Applicability | Design Drawings and Other Resources | Example Image (click to expand) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment Control Fence | Geotextile material supported by posts and trenched into the ground to support settling of sheet flows. |
|
||
| Filter Socks | Tubular mesh socks filled with wood chip or compost that dissipate flow velocities and pond water to promote sediment settling. |
|
||
| Natural Fibre Logs | Similar to filter socks but made of biodegradable materials such as coir, straw, or wood. |
|
||
| Rock Check Dams | Weir constructed across channels from granular material and geotextile to reduce flow velocity. |
|
||
| Vehicle Tracking Controls | Measures such as mud mats, shaker racks, or wheel washers to prevent vehicles from tracking mud offsite. |
Vehicle tracking controls:
Wheel washing:
|
||
| Sediment Dewatering Bags | Large geotextile bags used to filter sediment-laden water from pumped discharge. |
|
||
| Storm Drain Inlet Protection | Blocks sediment entry to inlets while allowing water through. |
|
||
| Sediment Traps | Runoff detention area created by an embankment or depression to allow sediment settling. |
|
||
| Sediment Ponds | Similar to sediment traps but larger. Excavated depression for permanent water retention |
|
||
| Weir Tanks | Tanks that detain stormwater runoff to promote sediment settling. |
|
||
| Polymer Flocculants | Chemical agents that bind suspended particles to enhance sediment removal. |
|
||
| Active Treatment Systems | Systems combining tanks, flocculants, and filters for precise and high-efficiency contaminant removal. |
|
Protecting LID features during construction[edit]
LID practices that promote infiltration as their primary function for water quality & management of overland flows - such as bioretention areas, permeable pavements, and infiltration trenches (link pages) - are vulnerable to damage during construction activities that can compromise their ability to function as intended.
These features can become clogged with sediment, experience erosion at inlets and in planted areas, suffer compaction from heavy machinery, or be contaminated by pollutants in construction runoff. To minimize these risks and maintain effective protection throughout all phases of construction, the following best practices should be implemented:
- Keep LID perimeter controls in working order throughout construction
- Protect LID inlets
- Avoid heavy equipment on infiltration areas (i.e., driving vehicles through filter beds, or over granular water storage and bedding layers
- Phase construction so that LID measures are constructed last. Underground LID features can be built early in the construction process, provided they are protected by a barrier such as a plug.
- Keep LID installations offline via flow diversion until construction is complete, the drainage area is stabilized, and vehicle mud tracking is stopped.
- Avoid using LID areas as temporary detention basins, but in cases where flow cannot be routed around LID areas, protection should be used to prevent accumulated sediment from migrating into the subgrade.
- Be mindful of stockpile locations relative to LID areas
- Inspect LID areas during ESC site inspections
- Identify and mark LID areas to increase awareness