LID opportunities on public land
Parks[edit]
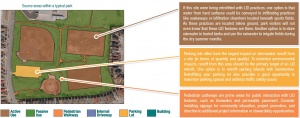
Parks range from simple parcels of municipal property to complex outdoor recreational facilities that include parking, sidewalks, trails, sports fields, field houses, operations facilities and washrooms. Each distinct area of your site can be a source for runoff (referred to as a ‘source area’). Target these areas when introducing LID in your park.
Targeting hard surfaces[edit]
Hard surfaces like parking lots and internal driveways are the most obvious targets for both stormwater quality and water balance improvements. These features produce more runoff than any other area on your site. Runoff from parking lots and driveways is typically more polluted than other source areas. Common water quality concerns include sand and salt from winter de-icing operations, hydrocarbons (gasoline) and heavy metals from vehicle breakdowns.
Runoff from vegetated areas of parks will be relatively clean and more closely matches the natural water balance. On municipal park properties, hard surfaces are usually located adjacent to pervious areas such as lawns, gardens or naturalized areas. This makes parks an ideal location for a LID retrofit. Where grading allows, you can construct bioswales and bioretention areas in these green areas to pre-treat water prior to infiltration.
You can also design parking surfaces and internal roadways as infiltration systems using permeable pavement. This retrofit strategy can be combined with other LID practices. Pathways paved with permeable paving are another LID option for your park. They reduce runoff volumes and encourage on-site infiltration. Exfiltration trenches are a viable option on many parks sites as well, as they provide an alternative to conventional conveyance systems (such as storm sewers). They encourage infiltration from hard surfaces and can be used to convey water to other LID features.
Accepting drainage from off-site areas[edit]
Does municipally owned land drain into your retrofit site? If so, this is an opportunity to provide stormwater controls for these areas. Roads are the most common source of runoff from external properties into parks. Treating municipal road runoff in a park requires planning input from municipal roads department staff. For these projects, the team must understand how all road activities, including winter maintenance and potential roadwork, will affect the operation of LID practices in the park.
Inter-municipal transfer of funds[edit]
Integrating LID practices into the municipal stormwater management framework may require a change in how municipal funds are managed. Traditional stormwater management maintenance resources and funds may have to be transferred to a more landscape-based stormwater management maintenance program. Instead of infrequent but expensive stormwater management pond sediment removal operations, time and resources would be spent on more frequent but inexpensive maintenance projects, including pruning and weeding bioretention practices or sweeping permeable pavement. Municipalities generally have the required staff and infrastructure within departments (e.g. arborists and horticulturalists in parks departments) to manage the maintenance of LID measures. However, funding this maintenance may require a transfer of funding and additional training. The federal Gas Tax Fund (GTF) is another funding option for funding LID retrofits. This federal transfer provides long-term funding for municipalities to build and revitalize public infrastructure. Up to 30% of a municipality's yearly GTF allotment can be used for stormwater management.
Source Areas[edit]
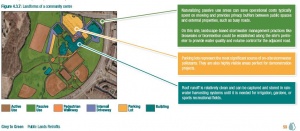
The best LID option for your site will depend what types of source areas are present. Source areas may include:
- Active use areas
- Passive use areas
- Pedestrian walkways
- Internal driveways
- Parking lots
On park sites, pollution prevention is often associated with changes to operations and maintenance practices and has not been included in the table below. Options and implementation strategies for a few of these source areas will give you some ideas for your park site.
| Source area | Permeable paving | Bioretention | Enhanced grass swales | Bioswales | Infiltration trenches and chambers | Exfiltration trenches | Landscape alternatives | Prefabricated modules |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active use area | ** | o | * | * | ** | * | o | o |
| Passive use area | o | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Pedestrian walkway | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | * | o |
| Internal driveway | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | o | * |
| Parking lot | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | o | ** |
Making it happen: Approaches to getting LID into parks[edit]
The scale of your LID project will largely determine how to proceed. While you can usually complete small-scale LID projects with in-house expertise and resources, large-scale projects require external support from consultants and contractors.
Small-scale projects[edit]

Starting with small-scale projects is a good strategy to increase public interest in LID practices, gauge municipal support and gain experience. Small-scale projects include retrofitting your park with landscape alternatives, rain barrels, or by using pollution prevention strategies and practices.
Small-scale projects require fewer resources and a smaller project budget:
- They do not require integration into capital works projects
- Engineering consultants are not required
- Contractors may not be not required
- External approvals are not required
- Consultation with the public is limited
Due to less financial commitment, it can be easier to build colleague support and to gain supervisor approval for small-scale projects. However, small-scale projects like landscape alternatives and pollution prevention may not be easily identified as LID practices by the public. Your project team should consider establishing educational signage to inform the public.
Large-scale projects[edit]
Large-scale projects require significantly more effort, budget, and staff than small-scale projects. Large-scale LID practices include:
- Bioretention
- Enhanced grass swales
- Bioswales
- Perforated pipe systems
- Permeable pavement
- Soakaways
- Infiltration chambers
- Rainwater harvesting
- Prefabricated modules
Consider a large-scale project if your municipality or department would like to be a leader in sustainability. Large scale projects are often highly visible and attract more public attention. Large-scale projects may also be the only solution to site-specific challenges. For example, if the parking lot on your site does not have existing stormwater controls, small-scale projects are not likely to fully achieve compliance with water quality and quantity objectives. Consider using an infiltration chamber or bioswale project to meet those objectives.
Before starting a large-scale retrofit project, consider the following distinctions that set these retrofits apart from small-scale projects.
Integration with capital works programs[edit]
Most large-scale LID retrofits must function with existing site infrastructure, such as storm sewers, catch basins and pavement systems. Constructing large-scale LID practices often requires these systems to be removed, exposed or replaced. Planned infrastructure replacement or rehabilitation projects provide opportunities for implementing LID practices. For example, if a planned project requires removing existing pavement, infiltration chambers, permeable pavement or bioretention can be incorporated. Budget and resources already set aside for infrastructure projects can be set aside for a retrofit project including replacement existing infrastructure.
Involvement of consultants and contractors[edit]
Consultants are required for large-scale retrofit projects, specifically for the final screening of options, pre-design, detailed design, tender and contract documents, construction supervision and administration, and assumption and verification. Site contractors are also required for large-scale LID retrofits.
Ideally, contractors should be pre-qualified based on previous experience with similar LID projects.
More intensive public consultation[edit]
Stakeholders must be closely involved in the retrofit process for large-scale LID projects. These projects have longer construction windows, may have significant impacts on long term public use patterns of the park, and will have significantly higher costs. Gaining public insight in advance of LID implementation can help address public concerns and information gaps, as well as identify public supporters and champions. Public consultation can help designers tailor the project to address community concerns and values.
External approvals[edit]
Large-scale park retrofits may require a variety of approvals at the municipal, watershed, provincial and/or federal level. Since LID is still relatively new, you may encounter policies or bylaws that present barriers to LID retrofit projects. Alternatively, the municipality may have to enforce some policies and bylaws to facilitate the implementation of LID projects within parks.
Municipal facilities[edit]
Each distinct area of your site can be a source for runoff (referred to as a ‘source area’). Target these areas when introducing LID in your municipal facility.
Targeting hard surfaces[edit]
Municipal facilities have large parking lots to accommodate public demand. Parking areas represent the most significant source of pollutant loading from these sites and contribute significantly to increased runoff rates in comparison to natural conditions. Parking lots include areas for parking, areas for driving, and islands or landscape planters used for calming traffic, directing vehicles and improving pedestrian safety.
LID practices can be incorporated into all areas of a parking lot. You can use bioretention in parking lot islands and along the lot perimeter. Standard curbs with small cut-outs (called ‘curb cuts’) can allow water to easily enter biorentention practices while also preventing damage from cars.
Bioswales are excellent options in parking lot islands or along lot perimeters. Parking lots with existing perimeter ditching are ideal for bioswale integration due to their extended continuous flow path.
Prefabricated modular infiltration chambers are gaining acceptance for their easy integration with parking lot functions. These subsurface systems are typically installed over a coarse granular reservoir to provide storage and allow infiltration into native soils. Infiltration chambers under conventional asphalt system work well on sites where parking demand and other site uses do not allow space for a stormwater feature.

Permeable pavements are also an option in large municipal parking lots. Pervious concrete, permeable interlocking concrete pavers, and porous asphalt can detain stormwater and increase infiltration.
Municipal facilities provide excellent opportunities for integrating rainwater harvesting systems. Rainwater harvesting systems have two requirements: an area for catchment of relatively clean runoff and a nearby demand for water usage. Municipal facilities often have large rooftop areas producing relatively clean runoff. Installing a cistern internal to the building or buried adjacent to the building can provide a sustainable source of water for site irrigation needs for landscaped areas, recreational fields and indoor use (e.g. flushing toilets and urinals).
Targeting highly visible areas[edit]
If your LID integration strategy involves highly visible LID practices, consider targeting areas with high-volume pedestrian traffic. This can help promote LID's visibility among the public and increase support for future LID projects.
Targeting pollution prevention opportunities[edit]
On some municipal sites, pollution prevention techniques and strategies are the best approaches to mitigating the environmental impact of your site. Retrofits of municipal works yards require a different approach than other land uses discussed in this guide. Works yards do not offer substantial opportunities for public interaction. LID retrofits should focus primarily on reducing pollution generated on-site. Fueling stations, waste storage areas, truck washing stations, sand and salt storage, staging areas and water conveyance features are ideal for pollution prevention.
Source areas[edit]
The best LID option for your site will depend what source areas are present. Types of source areas include:
- Active use areas
- Passive use areas
- Pedestrian walkways
- Internal driveways
- Parking lots
On municipal sites, pollution prevention is often associated with changes to operations and maintenance practices and has not been included in the table below.
| Source area | Permeable pavements | Bioretention | Enhanced grass swales / bioswales | Green roofs | Soakaways and infiltration chambers | Perforated pipe systems | Rainwater harvesting | Landscape alternatives | Prefabricated modules | Pollution prevention |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active use area | ** | ** | ** | o | ** | * | o | * | o | ** |
| Passive use area | o | ** | * | o | ** | ** | o | ** | ** | ** |
| Pedestrian walkway | ** | ** | ** | o | ** | * | o | * | * | ** |
| Internal driveway | ** | ** | ** | o | ** | ** | o | o | ** | ** |
| Parking lot | ** | ** | ** | o | ** | ** | o | o | ** | ** |
| Building | * | * | * | ** | ** | * | ** | o | o | ** |
Schools[edit]
| Source area | Permeable pavement | Bioretention | Enhanced grass swales / bioswales | Green roofs | Soakaways and infiltration trenches | Perforated pipe systems | Rainwater harvesting | Landscape alternatives | Prefabricated modules | Pollution prevention |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active use area | ** | ** | ** | o | ** | * | o | * | o | ** |
| Passive use area | o | ** | * | o | ** | ** | o | ** | ** | ** |
| Pedestrian walkway | ** | ** | ** | o | ** | * | o | * | o | ** |
| Internal driveway | ** | ** | ** | o | ** | ** | o | o | * | ** |
| Parking lot | ** | ** | ** | o | ** | ** | o | o | ** | ** |
| Building | * | * | * | ** | ** | * | ** | o | o | ** |