Difference between revisions of "Bioretention: Parking lots"
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) m (→See Also) |
Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) m (→See Also) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| − | *[[Bioretention: | + | *[[Bioretention: Streetscapes]] |
*[[Stormwater planters]] | *[[Stormwater planters]] | ||
*[[Rain gardens]] | *[[Rain gardens]] | ||
Revision as of 00:58, 13 March 2018
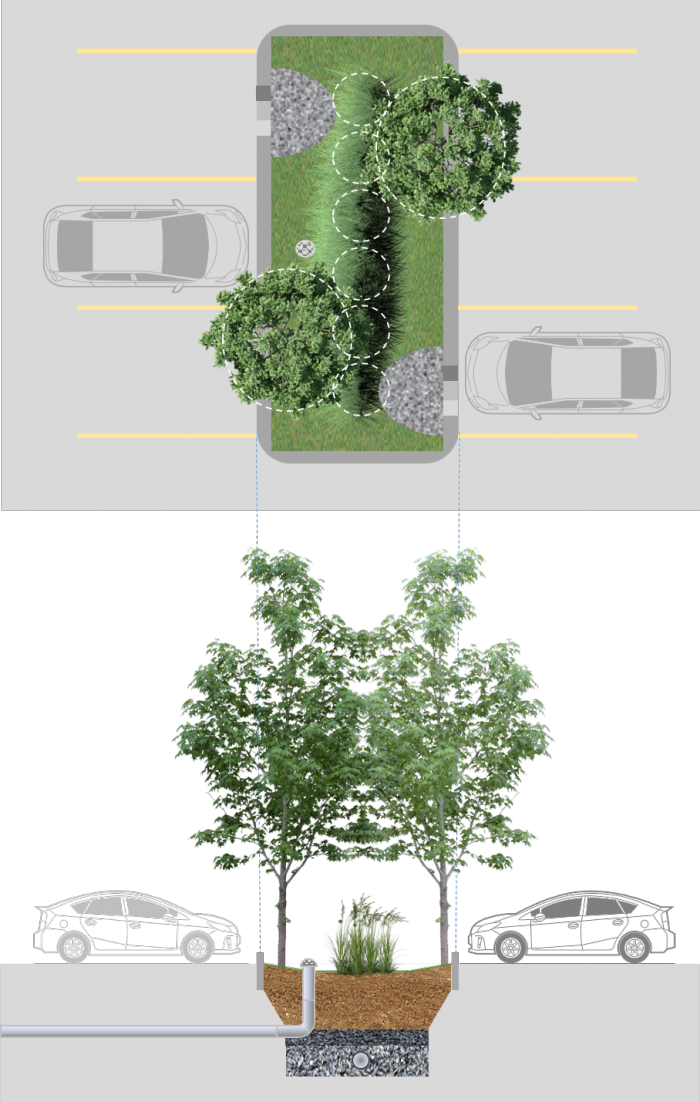
On commercial, industrial and multi-unit developments, a popular choice is to integrate bioretention into parking lot landscaped areas. These distributed cells typically accept sheet flow through multiple curb cuts, have shallow depression storage ≤ 100 mm, and a total area of 5 -200 m2. Although many parking lot schemes include long linear bioretention cells (≥ 0.6 m wide), infiltration is optimized by having a level grade and a level base, unlike a bioswale.
Gallery[edit]
Parking lot bioretention with surface ponding well in foreground, Kortright Centre, Vaughan, ON. Read about the performance of this practice in the technical brief.
Parking lot bioretention sharing underground reservoir with adjacent permeable paving, Edwards Gardens, Toronto, ON. Read a case study about it here.
Parking lot bioretention with decorative stone for erosion control, and perforated pipe access standpipe in foreground, Earth Rangers Centre, Vaughan, ON. Read about the performance of this practice in the technical brief.
The sunken curb holds the edge of the asphalt pavement and lets water freely flow to the bioretention cell beside the 7sigma parking lot in Minneapolis, MN (USA)
Photo credit:Brian AshBioretention cells on Elm Drive, Mississauga, ON, with vertical sides and hardscape perimeter receive road runoff via leader pipes from road catch basin inlets. Read about the stormwater system at this site in the performance assessment report.
Bioretention bump out in a dense urban setting receiving runoff via side inlet catch basin and curb openings on the walkway side of the installation.
Fairford Parkette featuring a bioretention cell retrofitted into a roadway in downtown Toronto, ON. Read a case study about it here.
Parking lot bioretention cell at IMAX corporate headquarters in Mississauga, ON. Read about the IMAX stormwater system in the performance assessment report
Bioretention cell receiving road runoff in the Wychwood neighbourhood of Brampton, ON. The nearby catch basin conveys overflows during major rain events. Read about the stormwater system in this community in the performance assessment report.