Aggregates
Revision as of 17:36, 23 January 2018 by Jenny Hill (talk | contribs) (Created page with " ==Reservoir Stone== thumb|Highest void ratio comes from having uniformly graded aggregate. File:Particle permeability.png|thumb|Higher perm...")
Reservoir Stone[edit]
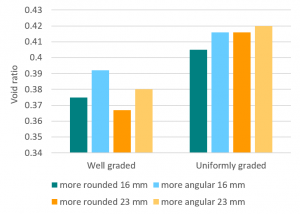
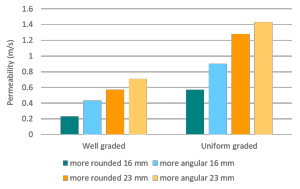
The important characteristics of the stone within the reservoir or underdrain are the lack of fines, the void ratio and (to a lesser extent) the permeability. Porosity and permeability are directly influenced by the size, gradation and angularity of the particles [1]
- ↑ Judge, Aaron, "Measurement of the Hydraulic Conductivity of Gravels Using a Laboratory Permeameter and Silty Sands Using Field Testing with Observation Wells" (2013). Dissertations. 746. http://scholarworks.umass.edu/open_access_dissertations/746